Table of Contents:
Automotive Prototyping Comprehensive Guide: From Concept to Reality
- November 23, 2024
- Tony
- Last updated on November 4, 2025 by Lucy
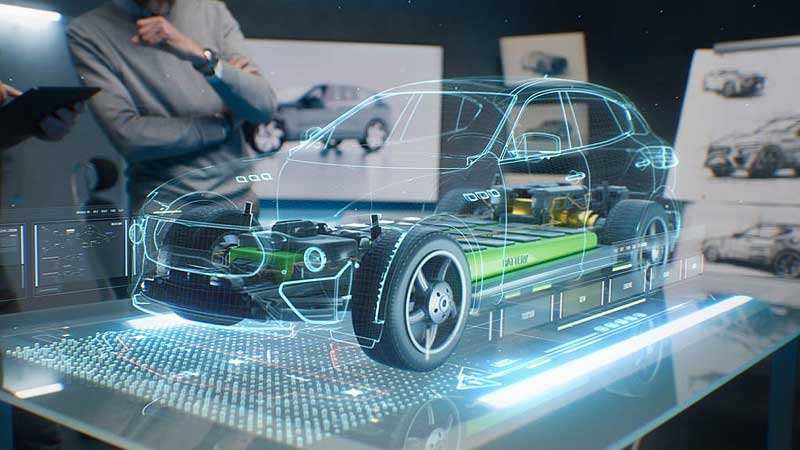

After years of deep immersion in automotive prototyping, I want to emphasize: Prototype vehicles are far more than simple models—they serve as the bridge between grand visions and exceptional automobiles. Allow me to reveal the truly critical elements that transform concepts into reality.
1. Automotive Prototyping Overview
1. What is automotive prototyping?

Automotive prototyping is the process of turning a conceptual design of an automobile into a real physical model through advanced manufacturing techniques.
Prototypes are usually used to test and verify the feasibility, performance and user experience of a design, and to provide a reference basis for subsequent mass production.
2. Why Prototyping Still Beats Digital Alone?
You Can't Beat Physical Testing
I’ve seen CAD models that looked perfect, but the first physical prototype revealed vibration issues no simulation could catch. Nothing replaces holding the part in your hand.
Speed to Market is Everything
While competitors are still designing, we’re already testing. I’ve helped startups go from sketch to working prototype in 3 weeks.
Cost Savings You Can Measure
Finding a design flaw in a $500 prototype beats discovering it in a $50,000 production run.
2. The core process of automotive prototyping
1. Conceptual Design Phase
Prototyping begins with the idea phase, which involves:

- Market Research:
Identifying user needs and analyzing competitors to guide the design process. - Sketching and Modeling:
Designers create sketches and digital 3D models to define the appearance and functionality of the vehicle.
2. Functional and Performance Validation Phase
Once a digital model is created, it is transformed into a physical prototype for thorough testing:

- Aerodynamic Testing:
Use wind tunnel experiments to optimize the car’s shape and reduce drag. - Structural Testing:
Evaluate the prototype’s durability and performance under extreme conditions like temperature fluctuations and pressure.
3. Iteration and Refinement Phase

Based on test results, adjustments are made to ensure the prototype aligns with both technical and aesthetic requirements. This stage brings the model closer to mass production standards.
3. Key technologies of automotive prototyping
1. Numerical Control Machining (CNC)

CNC machining is crucial for manufacturing precise, complex parts such as engine components and suspension systems, ensuring high accuracy during the prototyping process.
2. 3D Printing

3D printing accelerates the creation of intricate parts, reducing both time and costs, especially for components like headlight housings and interior trim pieces.
3. Melt and Die Casting

This technology is used to create metal parts with intricate shapes and smooth finishes, which is essential during the functional testing phase.
4. Virtual Simulation
Engineers use computer simulations to predict the prototype’s performance, minimizing errors during physical testing and optimizing the design process.
📌Case Study: Electric Vehicle Battery Mount
The Challenge: An EV startup needed 50 battery mounting prototypes for crash testing. The part had to withstand 20G impacts while being lightweight and cost-effective.
Our Solution: We used a hybrid approach combining CNC machining and 3D printing.
Prototyping Details:
- Material: 6061-T6 Aluminum (primary structure) + Carbon Fiber Nylon (brackets)
- Critical Requirements:
- Weight: Under 2.5kg complete assembly
- Strength: Survive 20G frontal impact
- Temperature range: -40°C to +85°C
- Vibration: 10-2000Hz without resonance
- Prototyping Approach:
- Main plates: CNC machined from solid billet
- Complex brackets: 3D printed carbon fiber nylon
- Fasteners: Production-intent hardware
- Finish: Powder coat for corrosion protection
- Testing Results:
- First iteration: Failed at 18G – resonance in bracket design
- Second iteration: Passed all impact tests
- Weight: 2.3kg (under target)
- Cost: 60% less than traditional tooling approach
- Timeline: 3 weeks from CAD to crash test
The breakthrough came when we identified the resonance issue through physical testing. No simulation had caught it because the damping characteristics of the 3D printed brackets differed from production materials.
4. Automotive Prototyping Material Selection

Aluminum alloys and stainless steel are often used for structural components like chassis and body frames, due to their strength and durability.
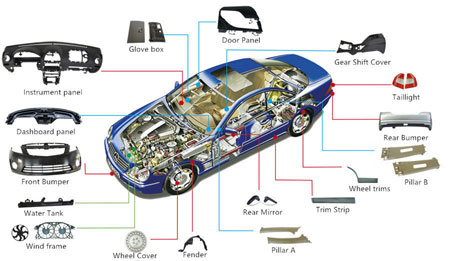
Lightweight plastics are commonly used for interior trims and non-load-bearing components, offering ease of manufacture.
For example:
- ABS: Good balance of strength and cost
- Nylon: Excellent for wear applications
- Polycarbonate: When you need impact resistance

Carbon fiber is preferred for high-performance vehicles because of its strength-to-weight ratio, especially in racing and luxury cars.
Ready to explore your material options? Dive into our comprehensive material properties guide, or connect directly with an expert for personalized guidance.
5. Common Prototyping Pitfalls and Solutions
The "It's Just a Prototype" Mindset
Problem: Treating prototypes as disposable Solution: Build every prototype as if it’s going to production – you’ll find real issues faster
Over-Engineering
Problem: Making prototypes more complex than needed Solution: Start simple, add complexity only when testing proves it’s necessary
Ignoring Production Reality
Problem: Designing parts that can’t be manufactured at scale Solution: Always consider how the part will be made in production
6. How to choose a reliable partner
Choosing the right automotive prototyping service provider is vital for project success. Focus on the following key factors:
Expertise and Experience
Select providers with extensive experience in automotive prototyping, a proven track record, and the ability to manage complex projects with innovative solutions.
Equipment and Capabilities
Ensure the provider has advanced equipment like CNC machines and 3D printers, along with skilled technicians to deliver high-quality results.
Effective Communication
Choose a supplier who understands your needs and offers clear, timely feedback to avoid misunderstandings and delays.
7. Future trends of automotive prototyping
Advancements in virtual simulation and digital twin technology will greatly enhance the efficiency and precision of automotive prototype development.
The adoption of eco-friendly materials, such as recyclable plastics and bio-based composites, will increase, aligning with the push for greener manufacturing practices.
Prototyping services will become more tailored to meet diverse market demands, emphasizing localized and flexible customization options.
Summary
Automotive prototyping is more than just bringing ideas to life; it serves as a crucial link between design, testing, and mass production. With the right processes, advanced technologies, and dependable partners, prototyping unlocks endless possibilities for the automotive industry.
For expert automotive prototyping services, trust the experienced team at Allied Metal to transform your innovative designs into cutting-edge products!
