Industrial-Grade 3D Printing Services
Precision additive manufacturing for brands and manufacturers. From rapid prototypes to small-batch end-use parts, we deliver high-integrity components in 7-10 days.
Trusted by Industry Leaders
3D Printing Capabilities
Advanced additive manufacturing technologies for diverse industrial applications
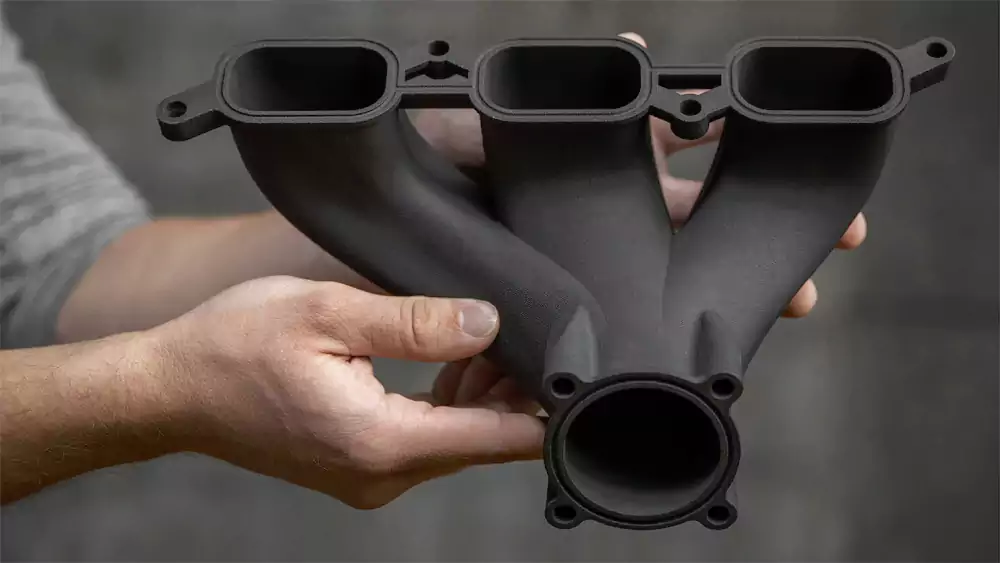

SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
High-strength functional parts with excellent mechanical properties. Ideal for complex geometries without support structures.
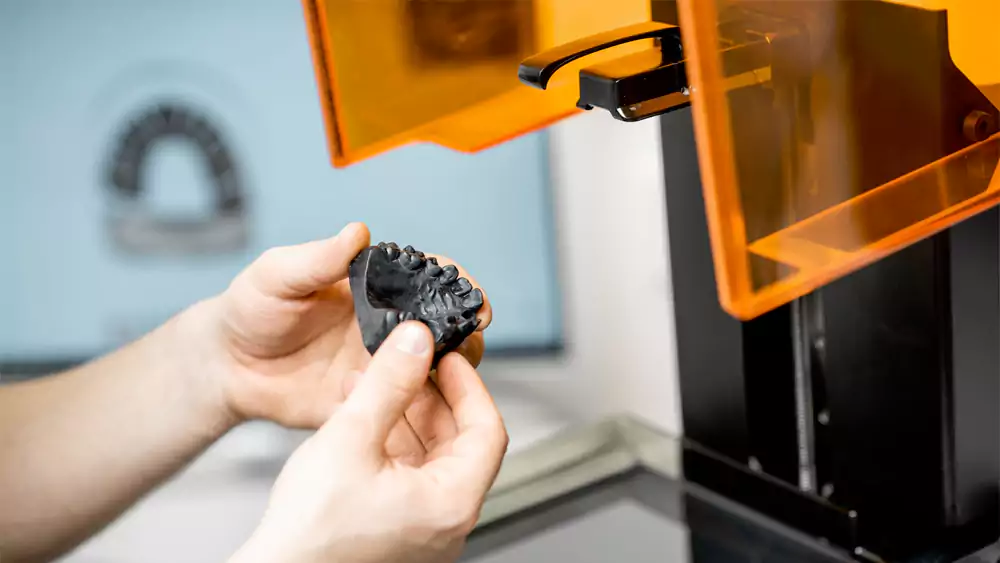

SLA (Stereolithography)
Ultra-high resolution for smooth surface finishes. Perfect for detailed prototypes and presentation models.
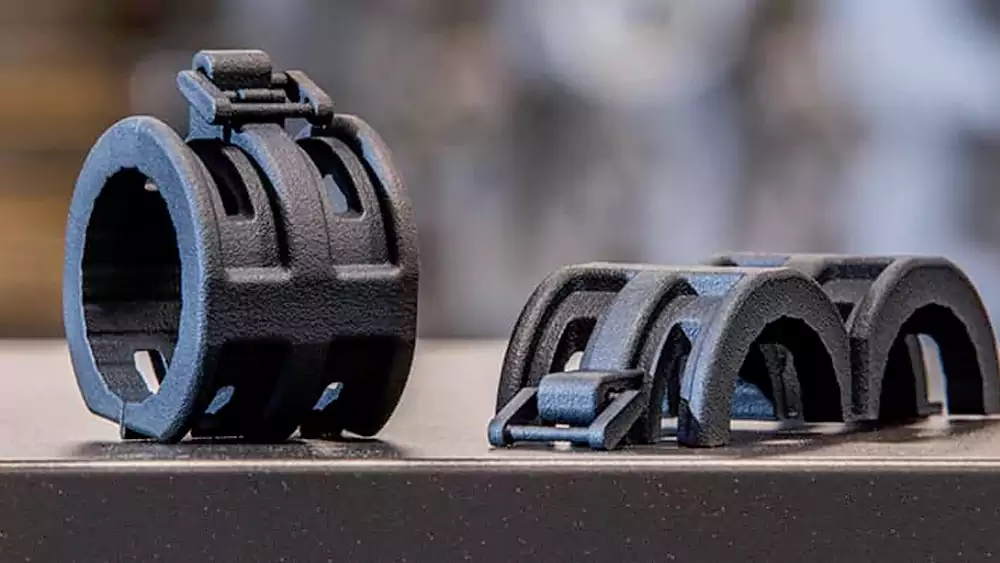

MJF (Multi Jet Fusion)
Production-grade parts with consistent mechanical properties and excellent surface quality at scale.
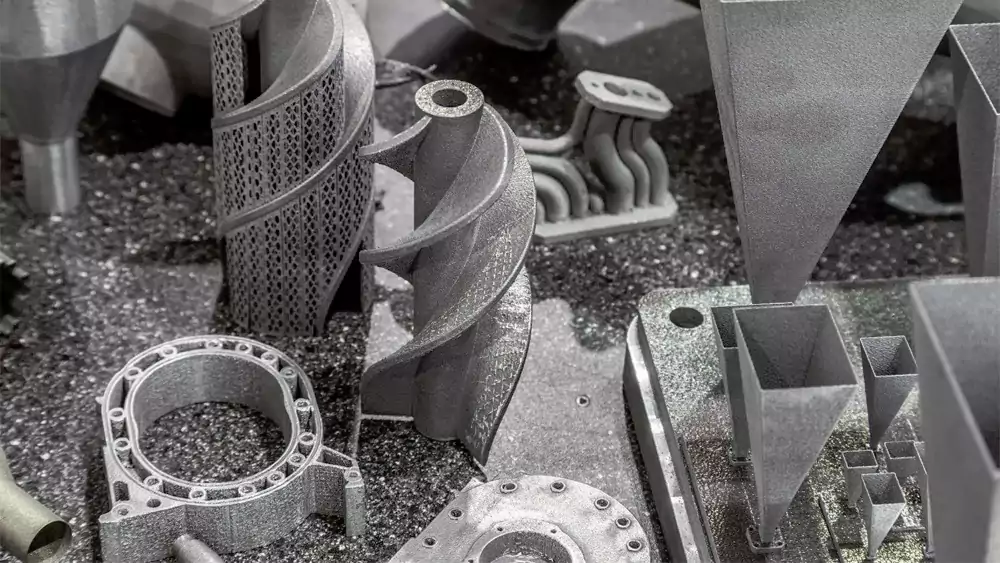
DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering)
Metal 3D printing for high-performance applications. Aerospace and automotive grade materials.
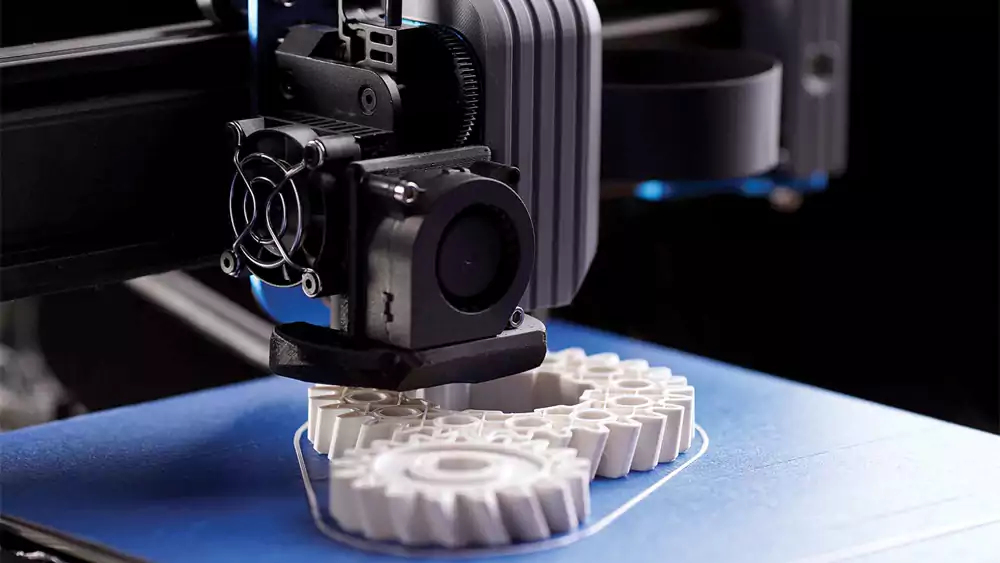

FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
Cost-effective prototyping and tooling with engineering-grade thermoplastics.

PolyJet Technology
Multi-material printing for realistic prototypes with varied properties in a single build.
Popular 3D Printing Materials
Choose from our extensive portfolio of industrial-grade 3D printing materials to meet your specific application requirements.
Plastics
(Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable plastic that is often used for low-stress applications. It is easy to use, and is often the material of choice for hobbyists and beginners due to its low cost and ease of use.
(Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a durable, heat-resistant plastic that is commonly used for prototyping and functional parts. It is easy to sand and paint, and can be used with a variety of 3D printing technologies. ABS plastic also allows for the color of the material to be accurately dyed.
Nylon is a strong, lightweight material that is often used for functional parts. It is highly durable and has a low coefficient of friction, making nylon the ideal material for parts that require wear resistance. Although nylon is typically seen in an off-white color, it’s ability to accept dyes allows a 3D printing service to make nylon in numerous colors.
(Polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified) is a strong and flexible plastic that is often used for parts that require impact resistance. It is also easy to print, and is often the material of choice for hobbyists and beginners.
(Thermoplastic polyurethane) is a flexible and elastic material that is often used for parts that require flexibility or elasticity. It is a durable material and has good chemical resistance, making it a good choice for parts that require flexibility and durability. TPU can not easily take color from dye but it works well with numerous types of paint.
Metals
Aluminum is a lightweight metal that is often used for parts that require low density and high strength. It is easy to machine and can be used in a variety of 3D printing technologies.
Stainless steel is a strong and corrosion-resistant metal that is often used for functional parts. It is easy to machine and has a low coefficient of friction, making steel an ideal material for parts that require wear resistance.
Titanium is a lightweight metal that is often used for parts that require high strength and stiffness. It is highly durable and has a low coefficient of friction, making it an ideal material for parts that require wear resistance.
Bronze is a strong and corrosion-resistant metal that is often used for functional parts. It is easy to machine and is often the material of choice for hobbyists and beginners due to its low cost and ease of use.
Silver is malleable, durable, and cost-effective. It is also highly conductive metal, making it ideal for electrical components. This metal material is also aesthetically pleasing making it an ideal choice for consumer grade products. Silver is also typically more environmentally friendly compared to its metal counterparts.
Specifications & Design Guidelines
Ensure your parts are designed for optimal manufacturability with our comprehensive design guidelines and specifications.
Technical Specifications
Design Guidelines
For optimal 3D printing results:
- Maintain minimum wall thickness of 0.8mm
- Design with self-supporting angles > 45°
- Include escape holes for powder removal (SLS/DMLS)
- Consider orientation for optimal strength
- Account for material shrinkage in critical dimensions
- Use fillets to reduce stress concentrations
Application Service Type
Whether you need new product development verification or personalized customization, please contact us and we can meet your needs

Popular 3D printing services
We can undertake personalized customization needs for various industries such as modeling, scanning, and printing.

Metal 3D printing
Can meet various needs of various metal materials, such as titanium alloy, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, mold steel, etc

Mold 3D printing
The products that can be applied to include key parts such as mold cores, inserts, sliders, sprue sleeves, etc

End-Use Parts
Produce final production parts with complex geometries and lightweight structures.
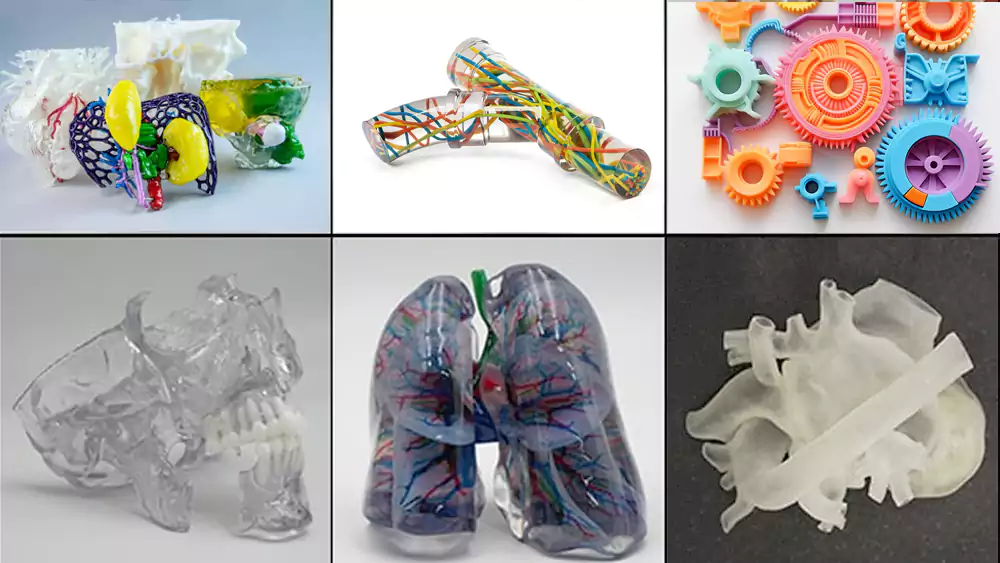
3D Printing Gallery
Explore examples of parts manufactured using our additive manufacturing technologies.
Customer Testimonials
See what our clients say about working with Allied Metal for their 3D printing needs.



Why Choose 3D Printing?
Additive manufacturing offers unique advantages over traditional manufacturing methods for specific applications.
Design flexibility
3D printing allows for the creation of highly complex and intricate designs that are challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Material waste reduction
Traditional subtractive manufacturing processes often generate significant material waste, as excess material is removed during machining. 3D printing is an additive process, where material is added layer by layer, resulting in minimal waste generation.
Rapid prototyping
3D printing accelerates the product development process by enabling quick and cost-effective prototyping. Design iterations can be rapidly produced and tested, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods.
Cost-effective production
3D printing can be cost-effective for low-volume or customized production. It eliminates the need for expensive molds, tooling, and setup costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
Why Choose Allied Metal for 3D Printing?
- Professional technology:
With advanced 3D printing equipment and technical team to ensure product quality. - Diverse materials:
Provide a rich selection of materials to meet different application needs. - Customer Service:
Personalized customer service, providing full support from design to production. - Continuous Innovation:
Continuously innovate technology, cost-effective and efficient.
When to choose 3D printing?
3D printing is an ideal choice for prototyping, small-scale production, and highly complex geometries. It allows for quick turnaround and minimal material waste, making it an excellent choice for custom parts. 3D printing is also well-suited for creating complex shapes, such as those with overhangs, that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
On the other hand, milling machines, lathes and other traditional manufacturing processes are better suited for large-scale production runs and parts with standard geometries, such as cylinders and cubes, because they are more cost-effective and are capable of producing parts quickly and efficiently at that production volume.

The process of 3D printing is not only rapid but also cost effective, allowing businesses to produce products with a high level of quality in a short amount of time.
3D printing also offers the flexibility to make changes to a design or prototype model quickly and cost-effectively, allowing businesses to respond quickly to changing customer needs.
If you are still not sure if ALLIED 3D printing is the right choice for your project needs simply email your files to our rapid project teams and they will review in detail for and with you, making recommendations along the way — quote@alliedcn.com
FAQ
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process that involves creating a physical object from a 3D CAD model. 3D printing is an additive process where layers of material are built up to create a 3D part.
It can use a variety of materials, such as plastics, metals, and ceramics, and is widely used in industry, medicine, and the arts. Click to view more details about 3D printing
3D printing technology originated in the 1980s and was initially used for rapid prototyping and prototyping;
As the technology developed, it began to be used in industrial design in the 1990s;
The 2000s saw a decrease in the price of equipment and an increase in the variety of materials, which led to widespread adoption across industries;
Entering the 2010s, 3D printing showed great potential in areas such as healthcare and aerospace, and open-source technologies allowed individual users to participate in innovation.
Today, combined with smart manufacturing and sustainability, 3D printing is continuing to drive progress across industries.
- Efficiency: Rapid production of complex shaped parts, shortening the product development cycle.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduce mold and production costs, especially suitable for small batch production.
- Design Flexibility: Enables personalization to meet user-specific needs.
- High material utilization: Reduced material waste through layer-by-layer printing, environmentally friendly.
The cost varies depending on the material, complexity and production lot. Generally speaking, small batch production will have more cost advantage.
The speed of printing is affected by the complexity of the design and the type of material, and can usually be completed within a few hours.
Using the right materials and printing techniques, 3D printed parts can have strengths comparable to traditional manufacturing.
Ready to Start Your Project?
Upload your CAD file for a free, instant quote or contact our engineering team for a design consultation.
