Last updated on October 23, 2025 by Lucy
Over the years, Allied Metal has helped hundreds of engineers and purchasing managers navigate the complexities of engineering plastics. Whether you’re working with PEEK, Delrin, or nylon, the right machining process is critical to both part performance and cost.

Advantages of Engineering Plastics in CNC Machining
What Are Engineering Plastics?

Engineering plastics are high-performance polymers known for their excellent mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability. They are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, electronics, automotive, and medical.
Differences Between Engineering Plastics and Ordinary Plastics

High Performance engineering plastics are stronger, more wear-resistant, and heat-resistant than ordinary plastics. While ordinary plastics materials like PVC and PP are used in everyday products, High Performance plastics such as POM, PTFE and PEEK excel in high-load, high-temperature, and demanding environments.
For example, PEEK maintains strength under extreme heat, while PTFE’s low friction and chemical resistance make it ideal for seals and electronic components.
Why Engineering Plastics Beat Regular Plastics?
Engineering plastics aren’t your everyday polymers. While regular plastics like PVC and PP work fine for simple applications, engineering plastics offer:
- Higher strength – they can handle serious mechanical stress
- Better heat resistance – some can withstand temperatures over 500°F
- Superior wear resistance – perfect for moving parts
- Chemical stability – they laugh off harsh environments
Think of it this way: if regular plastics are like pine wood, engineering plastics are like aircraft-grade aluminum.
Why Are Engineering Plastics Ideal for CNC Machining?
- High Precision: CNC machining ensures tight tolerances and accuracy for complex plastic parts.
- Superior Durability: Engineering plastics are more wear- and impact-resistant than standard plastics, making them ideal for demanding applications.
- Heat & Chemical Resistance: Materials like PEEK and PTFE maintain stability in extreme temperatures and corrosive environments.
- Lightweight & Low Friction: Lighter than metal and with a low friction coefficient, they are widely used in automotive, electronics, and medical industries.
- Efficient Machinability: CNC plastic machining minimizes material waste, enhances productivity, and ensures consistency in mass production.
With these advantages, engineering plastics play a crucial role in CNC machining and are widely used in manufacturing high-performance plastic components.
Common High Performance Engineering Plastics
POM: Strong and Wear-Resistant
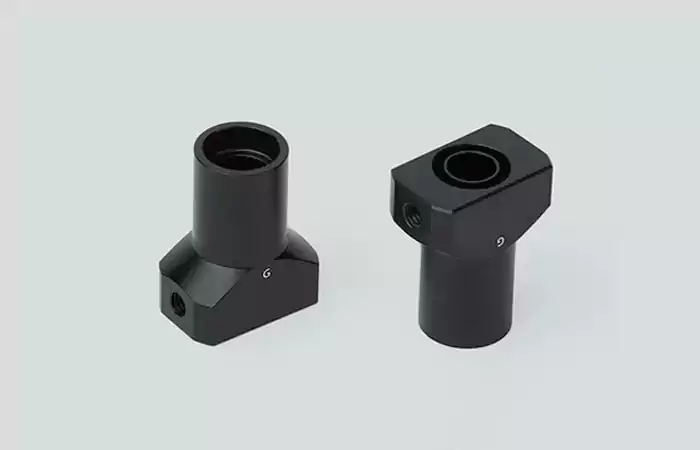

Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers high strength, low friction, and stability, making it ideal for gears, pulleys, and electronic connectors. It ensures smooth surfaces and minimal tool wear, commonly used in electronics and automotive parts.
PEEK: Heat and Chemical Resistant
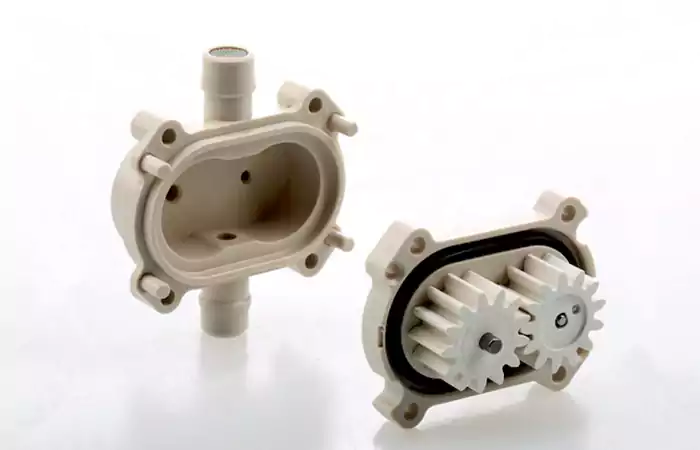

Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) withstands extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals, making it essential in medical and aerospace applications. Precision CNC machining prevents heat buildup and deformation, ensuring durability for critical components.
PA: Tough and Impact-Resistant
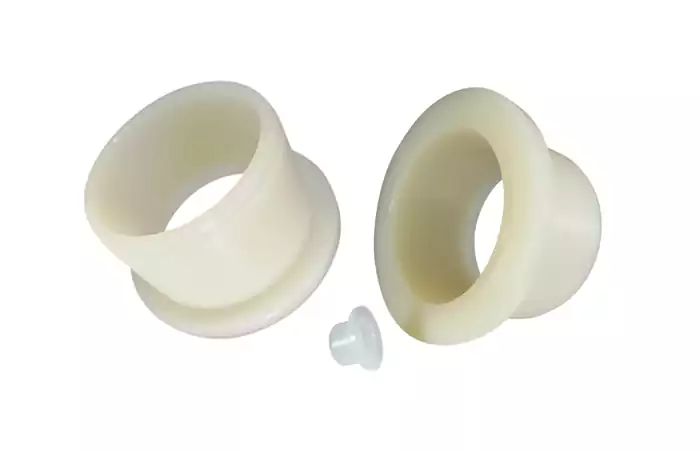

Polyamide (PA), also known as nylon, is highly wear-resistant and strong, ideal for bearings and automotive parts. Proper machining improves efficiency and reduces burrs, making it a key material in durable components.
PTFE: Low Friction and Chemical Resistant
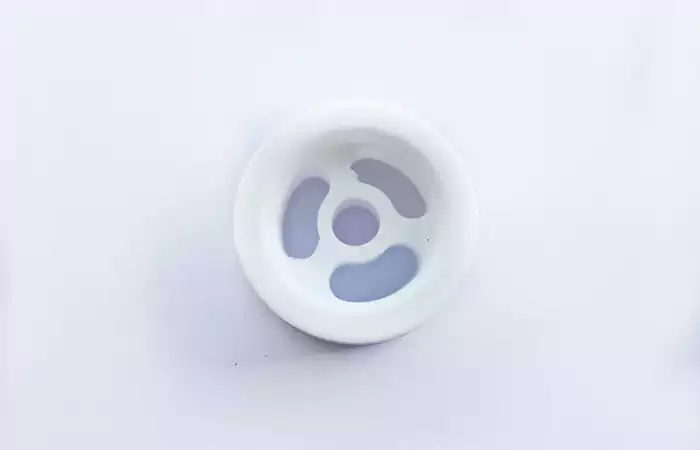

Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has ultra-low friction and excellent resistance to extreme conditions, making it perfect for seals and insulation. Sharp CNC tools ensure precision, widely used in medical and electronic industries.
PMMA: Transparent and Weather-Resistant
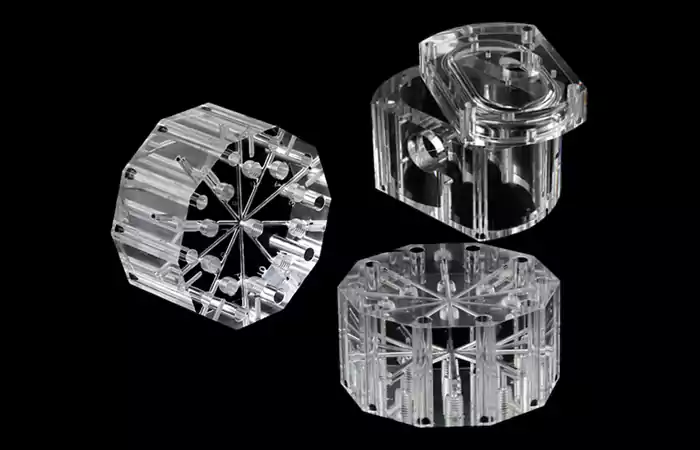

Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic, offers excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for display panels, lenses, and protective barriers. Precision CNC machining ensures smooth edges and minimizes stress cracks, widely used in automotive, medical, and signage applications.
How to choose the right plastic material for your part?
The following factors should be considered when selecting the right material for a particular application:
- Temperature resistance: PEEK maintains performance in high-temperature environments (up to 250°C), while POM handles normal operating temperatures effectively.
- Mechanical strength: PA and POM provide excellent rigidity and durability for structural components and load-bearing parts.
- Chemical resistance: PTFE offers superior performance in corrosive environments, while PVC suits general industrial applications.
- Optical clarity: PMMA delivers crystal-clear transparency for lenses, displays, and protective covers.
- Cost-effectiveness: POM often provides the best value when performance requirements allow, avoiding over-specifying with premium materials like PEEK.
What Parts Can Be CNC-Machined from Engineering Plastics?
You can use CNC machining to manufacture many different types of engineering plastic parts, including:
Medical devices
Dental surgical guides, cardiac implants, surgical tools, and medical equipment parts.
Industry parts (e.g., food equipment)
Nozzles, assembly line parts, conveyor belts, and food processing equipment components.
Semiconductor components
Electrical insulators, seals, electronic housings, and conductive parts.
Automotive and aerospace industry components
Fire dampers, valve seats, pump gears, automotive interior parts, and aircraft structural parts.
Marine components
Hull fittings, hatches, bulkheads, marine valves, and other parts.
🛠️ Case: Aerospace Cable Guide in PEEK
We had an aerospace client who needed cable guides that could withstand engine compartment temperatures while maintaining precise dimensional stability. Their previous supplier struggled with warping and cracking.
The Challenge:
- Material: PEEK (unfilled)
- Part: Cable guide with complex internal channels
- Temperature requirement: 250°C continuous
- Tolerance: ±0.05mm on critical bore dimensions
- Previous failure: 45% scrap rate due to thermal deformation
Our Solution:
- Used sharp 3-flute carbide end mills with polished surfaces
- Implemented trochoidal milling for internal channels
- Reduced RPM from 8000 to 5200 to control heat
- Increased feed rate from 0.08 to 0.12 mm/tooth
- Added compression cooling with chilled air at -10°C
- Stress-relief annealing between roughing and finishing
The Results:
- Scrap rate dropped from 45% to under 3%
- Achieved consistent ±0.03mm tolerance
- Surface finish improved from Ra 3.2 to Ra 1.6
- Tool life increased by 60%
- Total cost reduction: 32% compared to their previous supplier
The key was balancing heat management with efficient material removal – something we’ve perfected over hundreds of PEEK jobs.
Various CNC machining methods are ideal for different types of plastic parts:
CNC Drilling
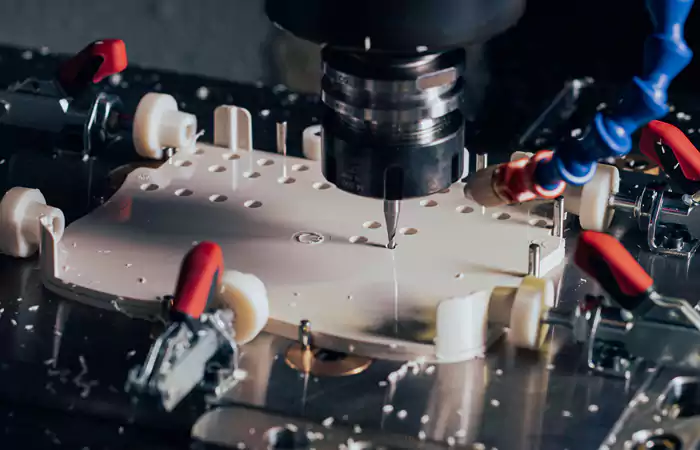
Precise drilling ensures the creation of holes for electronic components and mechanical parts, offering high precision and dimensional stability.
CNC Turning
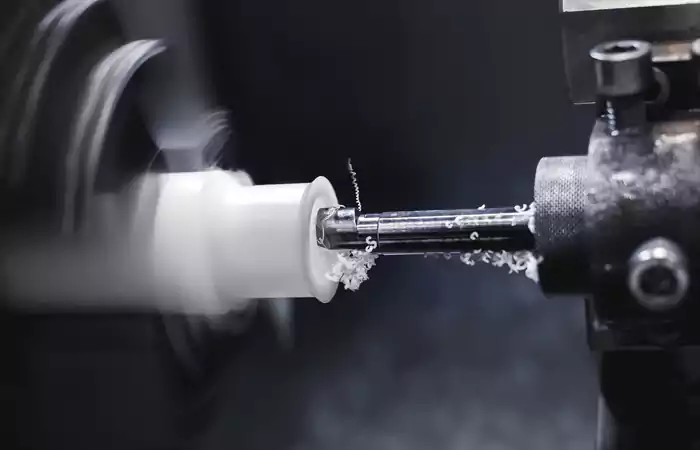

This technique is typically used for round or symmetrical parts, including bearings, gears, and pipe components.
CNC Milling
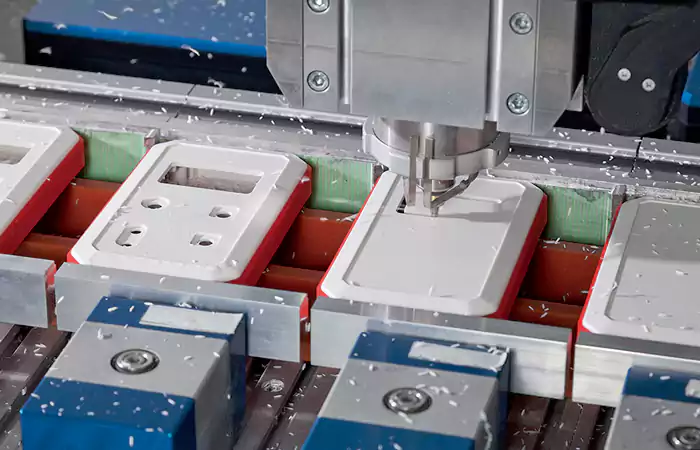

For parts with complex shapes, such as notching, cutting, and contouring, CNC milling is commonly used to machine gears, housings, and other precision components.
By combining these CNC machining methods with the unique properties of engineering plastics, manufacturers can meet the demands for high-precision and high-strength components across various industries.
FAQ for CNC machining of engineering plastics
Using coolant reduces the machining temperature, minimizing heat accumulation and preventing deformation.
Using coated tools helps reduce chip buildup, tool wear, and improves machining efficiency.
Optimizing the feed rate can improve PVC’s cutting quality and achieve a better surface finish.
Proper control of feed rate and cutting parameters reduces burr formation and enhances surface quality.
Lowering cutting speed, using the right tools, and improving cooling can reduce heat buildup and enhance machining precision and part quality.
Using low cutting speed, appropriate coolant, and selecting the right drill bit (such as a plastic-specific drill bit) reduces stress concentration and prevents cracks.
Future development trend of engineering plastics in CNC machining
The rise of environmentally friendly polymers
In the future, more degradable plastics and low-carbon manufacturing processes will be the focus of development.
Combination of 3D printing and CNC machining
Composite manufacturing technology can improve productivity and reduce costs.
Application of smart manufacturing
Data-driven CNC equipment will optimize machining parameters to improve the accuracy and consistency of plastic parts.
Summary
Engineering plastics are crucial in CNC machining for industries such as medical, electronics, and automotive. By selecting the right material and optimizing the machining process, both production efficiency and part quality can be improved. With the rise of intelligent manufacturing, the potential for engineering plastics in CNC machining will continue to expand.
