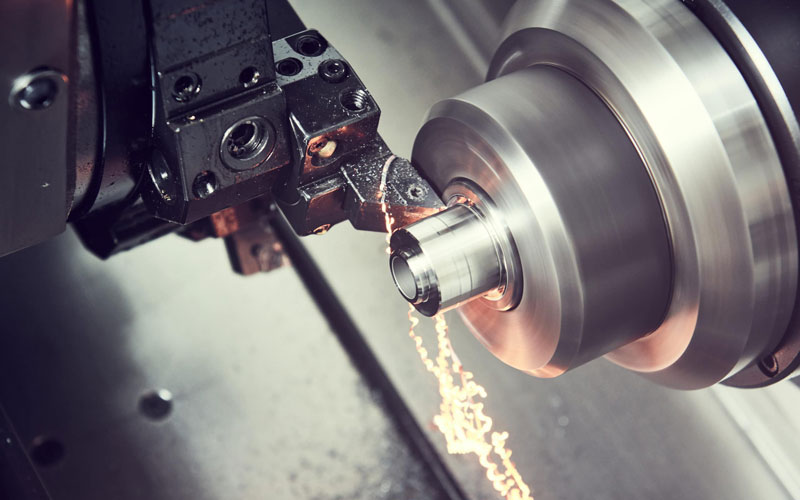
Composite Parts Machining
Allied Metal – Your trusted partner for precision composite parts machining, combining cutting-edge technology with expert craftsmanship.
- Source Factory
- Reasonable price
- Certified Materials
- Timely delivery
Composite Parts Machining
Composite materials are changing the manufacturing landscape due to their high strength, light weight and versatility. As more and more industries begin to adopt these materials for high-performance applications, it is important to understand the properties of composites and how they are machined.
Allied Metal offers specialized composite part machining services to ensure the precision and quality required by a variety of industries.

Common Composite Materials
Material Name | Properties | Applications | |
 | Carbon Fiber | Lightweight, high strength | Aerospace parts, automotive components |
 | Fiberglass | Durable, corrosion-resistant | Marine equipment,Aircraft/ automotive structural parts |
 | Kevlar | High tensile strength, impact resistant | Electronic equipment/automotive/protective equipment parts |
 | Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) | High stiffness, fatigue resistance | Aircraft structures, sporting goods |
 | Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) | Cost-effective, strong | Construction, marine industries |
 | Thermoplastic Composites | Recyclable, lightweight | Automotive interiors, consumer electronics |
Advantages of composites:
- Lightweight: composites offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios.
- Durability: They resist corrosion and wear and can handle harsh environments.
- Versatility: the properties of composites can be adapted to the needs of the application.
- Low long-term cost of ownership: Lower maintenance requirements and long life reduce life cycle costs.
- Design Flexibility: Composites are structurally designable, allowing materials to be engineered with specific properties as needed.
How to choose the right material?
- Consider the application requirements: What is the purpose of the part? Is strength or lightweighting required?
- Evaluate environmental factors: Will the material be exposed to moisture, chemicals or high temperatures?
- Evaluate mechanical properties: Select a material based on the strength, stiffness and durability required.
- Balancing cost and performance: Find a balance between material performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Recyclability: For environmentally conscious industries, prioritize recyclable thermoplastic composites.
Which industries benefit from composites?
Carbon fiber composites are widely used in aircraft fuselage and wing structures due to their high strength and light weight. This not only reduces the weight of the aircraft, improves fuel efficiency and range, but also enhances the overall performance and safety of the aircraft.
Fiberglass and carbon fiber composites are commonly used in automotive bodies, hoods and interior components. These materials reduce vehicle weight, improve fuel economy and handling, and increase safety in a crash.
Carbon fiber and fiberglass composites are used in a large number of motorcycle frames, exhaust systems and exterior panels. These materials make motorcycles lighter, increase speed and fuel efficiency, while enhancing vehicle rigidity and impact resistance, providing riders with a better handling experience.
Carbon fiber and polymer matrix composites are used in the manufacture of medical devices such as prosthetics, surgical instruments and stents. These materials are biocompatible, lightweight and strong, improving patient comfort and reducing the weight of devices while increasing their durability and precision.
Fiber Reinforced Plastics (FRP) are commonly used in bridge reinforcement, facade and roof design. the corrosion resistance and high strength of FRP make buildings more durable in harsh environments, reducing maintenance costs and improving safety.
Fiberglass composites are widely used in the manufacture of boat hulls, decks and masts. The materials are corrosion-resistant, lightweight and resistant to salt water and high humidity in the marine environment, extending the life of the vessel while improving sailing efficiency.
Comparison of common composite parts machining
Name | Principle | Advantages | Suitable Batches | Requires Mold | Manufacturing Cycle | Precision | Surface Roughness | Cost Analysis |
CNC Turning | Rotating cutting tool removes material | Efficient and precise, ideal for cylindrical parts | Small to medium batches | ❌ | Short | ±0.01 mm | Smooth | Moderate cost, limited to simpler shapes |
CNC Milling | Multi-axis cutting | Handles complex shapes with high precision and flexibility | Small to medium batches | ❌ | Short | ±0.01 mm | Smooth | Higher cost, suitable for small to medium batches of complex parts |
CNC Milling | Focused laser beam melts material | Fast and precise, suitable for thin sheets and complex designs | Small to medium batches | ❌ | Small to medium batches | ±0.05 mm | Smooth | Moderate cost, ideal for customization and small batch production |
Sheet Metal | Forming material through bending, stamping | High strength, ideal for large metal parts | Large batches | ✔ | Medium | ±0.01 mm | Variable | Lower cost, suitable for mass production |
Investment Casting | Pouring molten metal into a mold | Ideal for complex shapes with high surface finish | Large batches | ✔ | Long | ±0.05 mm | Smooth | High initial mold cost, but economical for large-scale production |
3D Printing | Layer-by-layer material addition | No molds required, flexible for complex shapes and prototyping | Small batches and rapid prototypes | ❌ | Short | ±0.1 mm | Variable | Higher cost, ideal for prototyping and customization |
Injection Molding | Injecting molten plastic into a mold | Highly efficient for mass production with excellent part | Large batches | ✔ | Medium to Long | ±0.1 mm | ±0.1 mm | High mold cost, but low unit cost for large-scale production |
Why choose Allied Metal for Composite Parts Machining?

We have an experienced team that can provide professional material and machining suggestions.

We have modern CNC equipment, laser cutting machines and 3D printers to ensure quality results.

We provide a full range of customized services from design to production to meet your different needs.

From design to production, Allied Metal provides comprehensive support at every stage of composite machining.
FAQ
Composites are engineered materials made from a combination of two or more different materials designed to achieve superior performance.
Composites are typically composed of a matrix (which acts as a bond) and reinforcements (which provide strength and rigidity). Common matrices include polymers, metals and ceramics, while reinforcements are usually carbon or glass fibers, for example.
Materials are selected based on the strength, weight, and environmental requirements of the part in conjunction with budgetary considerations.
No. The use of specialized equipment such as CNC machines and waterjet cutters ensures minimal material damage.
It depends on the complexity and processing method. CNC machining and laser cutting are faster, while molding has a longer cycle time.
Composites are lighter, corrosion-resistant, and can be customized to meet specific needs, while metal offers greater structural strength.






