20 common machining alloy metals and their properties
- November 19, 2024
- Tony
- Last updated on October 30, 2025 by Lucy
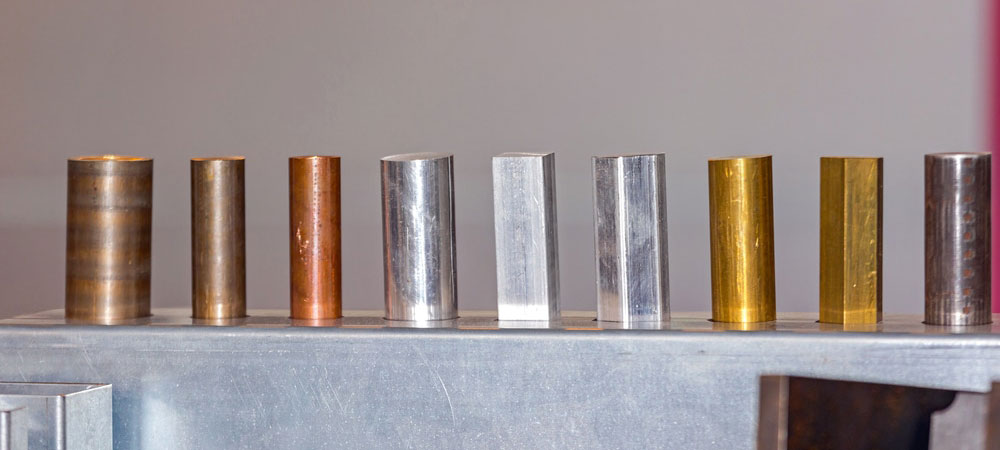

Alloy metals are indispensable materials for modern manufacturing industries due to their excellent mechanical properties and versatility. Understanding the characteristics, compositions and processing methods of alloy metals can not only help choose the right material, but also improve processing efficiency and product quality.
1. What are Metals?
Metals are materials that conduct electricity well, can be bent or stretched (ductility), and handle compression—making them essential in manufacturing. We split them into two main types: ferrous and non-ferrous.

1.1 Ferrous Metals
Ferrous metals are mainly composed of iron, including steel and cast iron, and are characterized by high strength and good hardness, but poor corrosion resistance.
1.2 Non-ferrous Metals
Non-ferrous metals, including aluminum, copper, and magnesium, are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, and are the materials of choice for the aerospace and electronics industries.
In terms of properties and applications, ferrous metals such as iron and steel are the primary materials used to build infrastructure and manufacture machines, while non-ferrous metals are used to make components and products with specific performance requirements due to their unique physical and chemical properties.
2. What are alloy metals?

Alloyed metals are materials made by mixing two or more elements, at least one of which is a metal. Alloys achieve improved properties by optimizing their composition, such as the addition of chromium to stainless steel to increase corrosion resistance.
3. Alloy metals compositions and their properties.
The properties of an alloy depend on its composition. The following are common alloying elements and their properties:
Enhances strength and hardness and is a major component of ferrous metals.
Increases hardness and resistance to wear, used in tool and structural steels.
Lightweight and corrosion resistant, used in aerospace alloys.
High temperature and corrosion resistant, used in turbine engines and chemical equipment.
Improves wear and corrosion resistance, mostly used in stainless steel.
Enhanced conductivity and corrosion resistance, commonly used in electrical equipment.
High strength and light weight, ideal for aerospace and medical industries.
Enhances hardness and toughness, used in high-strength steels.
Improves electromagnetic properties, common in silicon steel and electronic alloys.
Increases high-temperature hardness and wear resistance, used in tool steels and high-temperature alloys.
4. Advantages of Alloy Metals.
Alloy metals are the modern machining materials of choice because of their excellent properties. The main advantages include:
- Higher strength and hardness: e.g. high strength steels are used in bridges and high-rise buildings.
- Lighter weight: Aluminum alloys are used in aircraft construction to reduce weight and improve performance.
- Superior corrosion resistance: Stainless steel excels in chemical equipment.
- High temperature resistance: Nickel-based alloys are used for high-temperature components in aircraft engines.
- Good electrical and thermal conductivity: copper alloys are widely used in the electrical industry.
- High wear resistance: tool steel is suitable for making cutting tools and molds.
- High customizability: by adjusting the composition, the alloys can meet different industrial needs.
5. 20 common machining alloy metals.

Composed of iron and carbon, high strength and good toughness, suitable for construction, automobile and machine parts manufacturing.

Contains chromium and nickel, strong corrosion resistance, widely used in kitchen equipment and medical equipment.

lightweight, corrosion-resistant, composed of aluminum and magnesium or silicon, preferred for aerospace and automotive manufacturing.

Composed of copper and zinc, copper alloys are aesthetically pleasing and very conductive, often suitable for electrical connectors and decorative materials.

Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin with good wear and corrosion resistance, mostly used for bearings and ship parts.

Lightweight and strong, composed of titanium and aluminum or vanadium, widely used in aerospace and medical fields.

Extremely light, consisting of magnesium and aluminum or zinc, used for automotive parts and electronic equipment housings.

Excellent resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, suitable for use in turbine engines and chemical equipment.

High hardness, wear resistance, with good toughness, for cutting tools and mold making.

Designed for extreme high temperature environments, commonly used in jet engine components.

Low melting point, easy to cast, widely used in the manufacture of a variety of instrument housings, automotive parts housings, bearings and other complex shaped parts.

Lightweight, wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant and high thermal conductivity, suitable for engines and heat exchangers, sliding friction conditions used in parts.

Chrome alloys have a high melting point and good resistance to oxidation and corrosion. It has a wide range of applications in the aerospace, automotive, and metallurgical industries.

Because of its low melting point, excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, it has a wide range of applications in many fields, such as electronics, machinery and packaging.

Excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, mostly used in medical, industrial, chemical and marine engineering.

High strength and good thermal conductivity, used in electronic equipment, aerospace and high-precision molds.

Commonly used in transformers and motors due to superior electromagnetic properties and widely used in the power, electronics and military industries.

High strength, good toughness and wear resistance, extensive machinability, commonly used in automotive, machinery and construction industries.

Low thermal conductivity, good magnetic conductivity, high temperature and low temperature stability, mostly used in electrical and electronic equipment and aerospace.

Excellent superconductivity and good processing performance, mostly used in high-tech equipment and research experiments as well as medical and military undertakings.
6. Common Alloy Metals Machining Methods.
Alloy metals are machined in a variety of ways, the following are a few common machining methods:
- CNC machining:
Suitable for precision machining of complex parts, such as titanium alloys and nickel-based alloys. - Investment mold casting:
High-precision molding process, commonly used for copper alloy and stainless steel parts. - 3D printing:
Suitable for small batch customization and lightweight structural materials, such as aluminum and magnesium alloys. - Forging and Stamping:
Enhance material strength and toughness, suitable for tool steels and high temperature alloys. - Turning and Milling:
Widely used for machining standard mechanical parts, such as carbon steel and aluminum-silicon alloys.
📌Case Study: CNC Machining a Titanium Alloy Aerospace Bracket
Background: A client needed a custom bracket for satellite deployment mechanisms—lightweight, strong, and able to handle extreme vibration.
Material Selected: Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5 titanium alloy)—chosen for its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
Machining Process: We used 5-axis CNC milling to handle complex angles and tight tolerances.
Key Parameters:
- Dimensions: 120mm length × 80mm width × 15mm height
- Tolerance: Held to ±0.02mm across all critical features
- Surface Finish: Electropolished to Ra 0.4 μm for reduced friction and better fatigue life
- Production Volume: 50 units delivered in 3 weeks
Challenge: Avoiding tool wear due to titanium’s toughness—we switched to carbide end mills and optimized coolant flow.
Outcome: The brackets passed all stress tests and reduced the client’s assembly weight by 20%. This kind of job is why we keep Ti-6Al-4V in stock—it’s a beast for high-stakes applications.
7. Summary(alloy metals)
Alloy metals are the backbone of today’s manufacturing—offering performance and flexibility. From steel beams to titanium implants, knowing these materials inside out helps us pick the right one and machine it efficiently. At Allied Metal, we’ve seen it all over the years, and that experience translates into better parts for you.
