Precision CNC Shaft Solutions
High-precision shaft manufacturing for automotive, medical, and industrial automation. From rapid prototypes to full-scale production, Allied Metal delivers strength and accuracy you can depend on.
Precision CNC shafts depend on the right type, material, design, machining, and finish to ensure performance and reliability.This is why I always begin with clear classifications and careful design before cutting any metal.
Shaft Types & Classifications
The first step in custom manufacturing is identifying the right type of shaft for your application’s specific load and function requirements.
Straight Shafts
Straight shafts are the most common. They can be divided into spindles, axles, and transmission shafts. A spindle supports parts and transfers both torque and bending moments. An axle supports rotating parts but does not transmit torque. A transmission shaft transfers torque between components like gearboxes and wheels.
- Spindles: Support rotating parts and only transmit bending moment (e.g., front wheel axle of a bicycle).
- Transmission Shafts: Primarily transmit power and withstand torque, with minimal bending moment (e.g., automotive driveshafts).
- Rotating Shafts: Support parts and transmit power, enduring both bending and torque (e.g., motor shafts, machine tool spindles).
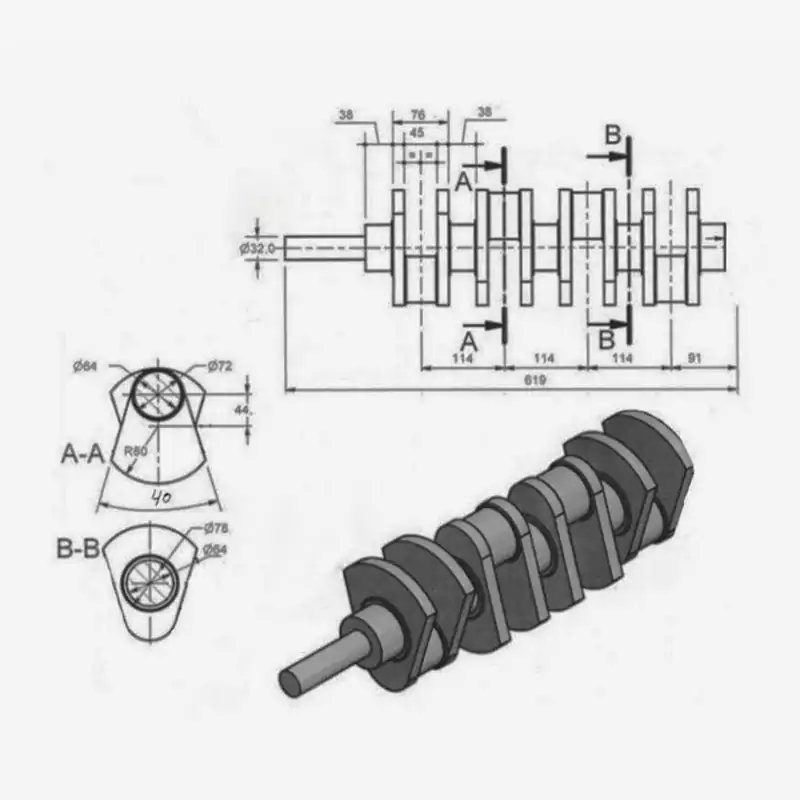
Crankshafts
Crankshafts convert reciprocating motion to rotational motion. I often see them in engines, compressors, and pumps. They endure high bending and torsional stresses, so the machining needs exact alignment.
Flexible Shafts
Shaft Materials
Custom shafts are commonly made from carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, or lightweight metals like aluminum and titanium. Material selection is critical for shaft performance, dictating its strength, durability, and cost. At Allied Metal, we leverage our deep material science knowledge to help you choose the ideal metal for your project, from cost-effective alloys to high-performance superalloys.
Carbon & Alloy Steels
Stainless Steels
Aluminum Alloys
Used when light weight is a primary concern without sacrificing significant strength. Common in robotics and aerospace.
Titanium
In addition to the common materials used for the above shaft products, we can also process various special alloy materials. If you have other material requirements, please visit our materials page for details or contact us directly for further information and a quote.
Structural Design & Axial Positioning
A shaft’s reliability depends on its structural design and the precise positioning of components like gears, bearings, and pulleys. We provide free DFM analysis to optimize your design for performance and manufacturability.
Key Design Considerations:
Our engineering team collaborates with clients to perfect shaft geometry, ensuring stress concentrations are minimized and parts are securely fixed.
Used to create a positive stop for bearings and gears, providing precise axial location.
A cost-effective method for axially securing components without needing a full shaft step.
Machined features that transmit torque from the shaft to a component like a gear or pulley.
Provide strong, adjustable axial clamping force for securing bearings and other critical parts.
Our Integrated Machining & Finishing Process
We offer a complete, one-stop solution, from raw material to finished, treated, and inspected high-performance shafts.
Custom Shaft Machining Process
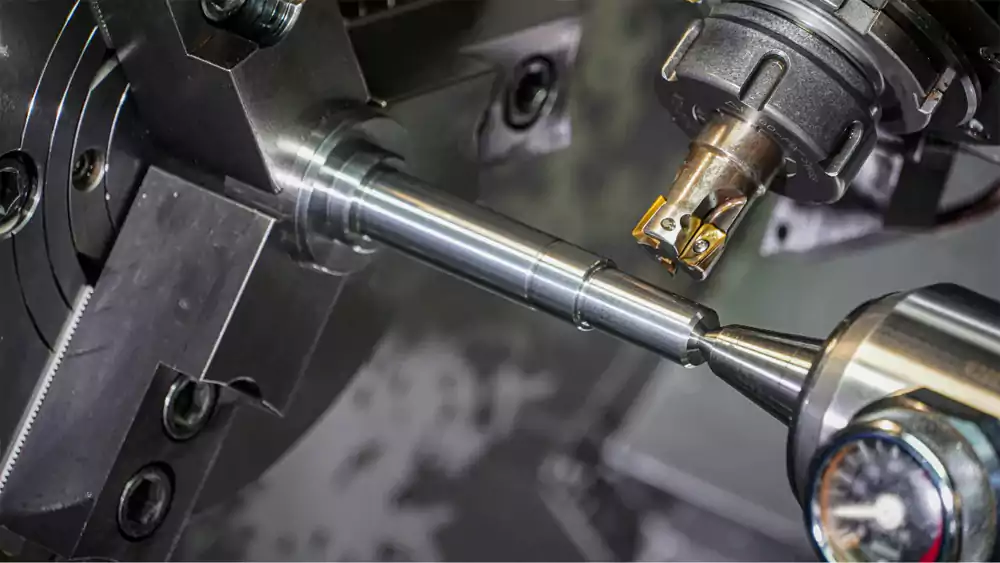

Our state-of-the-art facility utilizes a multi-step process to ensure ultimate precision:
- CNC Turning: Forms the primary diameters, steps, and profiles of the shaft.
- CNC Milling: Creates features like keyways, flats, and holes using our 3, 4, and 5-axis machines.
- Grinding: For applications requiring extremely tight tolerances and superior surface finishes on bearing journals.
- Quality Inspection: CMMs, optical projectors, and material testers verify every feature against your drawing.
Shaft Surface Treatments
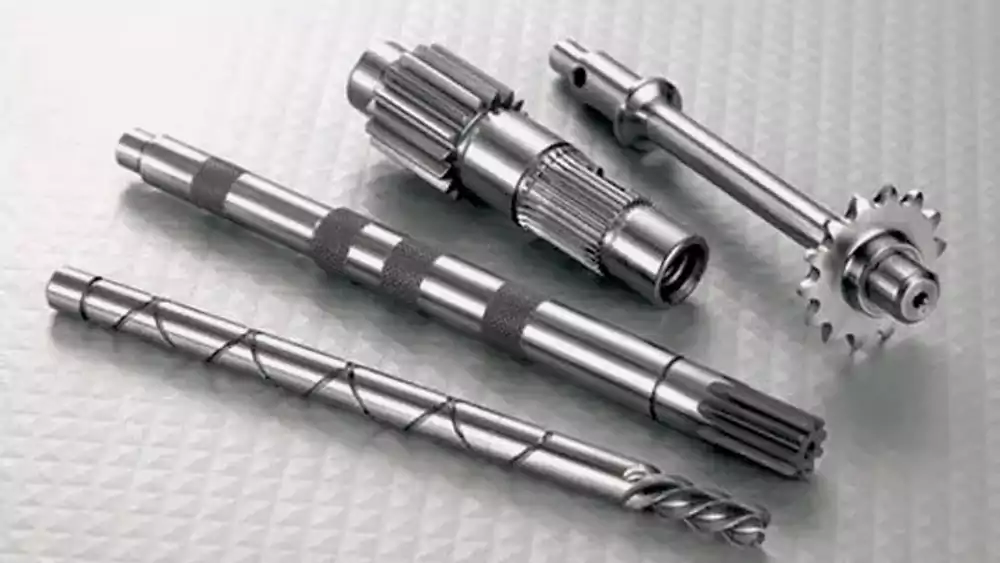

Surface treatment is crucial for enhancing a shaft’s wear resistance, hardness, and corrosion protection.
- Heat Treatment (Hardening): Significantly increases the hardness and strength of steel shafts.
- Case Hardening: Hardens only the surface layer for wear resistance while keeping the core ductile.
- Plating (Chrome, Nickel): Adds a hard, corrosion-resistant layer.
- Polishing: Creates a smooth surface to reduce friction and improve the fit of bearings and seals.
Looking for a more comprehensive guide beyond CNC axis machining? Explore our Ultimate CNC Machining Guide, where I detail every step from raw materials and design to processes and final customized parts.
Design & Manufacturing Considerations
Partner with us to navigate critical design choices that impact performance and cost. Our free DFM consultation is key to avoiding common pitfalls.
Engineering for Success:
We help clients balance design intent with manufacturing reality.
Tolerance Stack-up:
We analyze how individual part tolerances affect the final assembly's fit and function.
Material vs. Cost:
We guide you in selecting a material that meets performance specs without over-engineering and increasing costs.
Stress Concentration:
We recommend adding fillets and radii at diameter changes to reduce stress points and prevent fatigue failure.
Surface Roughness (Ra):
We help you specify the appropriate surface finish for functional areas like bearing seats and seal surfaces.
Case Studies: Precision Shafts in Action
We manufacture critical components for industry leaders. Here are some examples of the shafts we produce.
Automotive Transmission Shaft
High-Performance Transmission Shaft
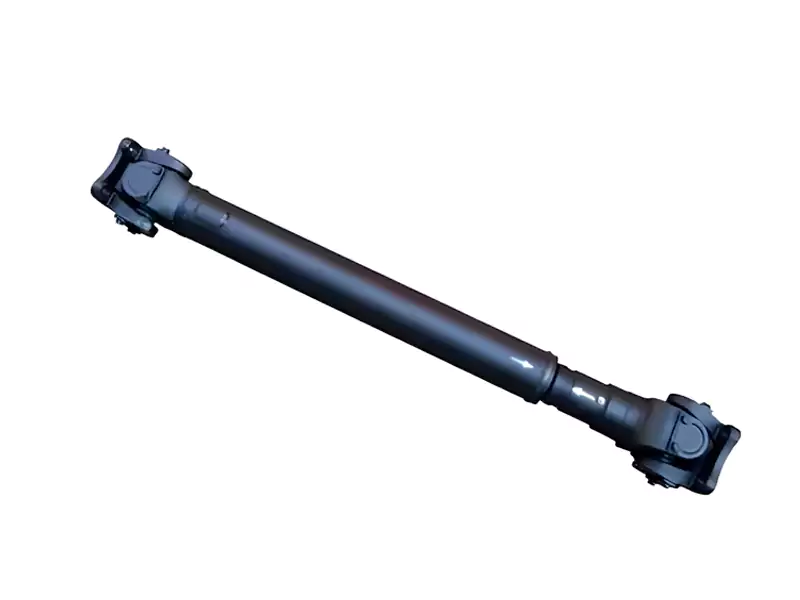

- Problem
A leading automotive manufacturer needed transmission shafts capable of handling increased torque requirements in their new performance vehicle line. Their previous supplier struggled with maintaining dimensional stability and surface finish quality at production volumes.
- Solution
Allied Metal implemented a specialized CNC turning process with integrated grinding operations. We developed a custom fixturing solution that reduced vibration during machining, resulting in superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
±0.0002″
Diameter Tolerance
0.8µm
Surface Finish (Ra)
99.7%
First-Pass Yield
50,000+
Units Produced
Material: 4140 Alloy Steel, Hardened to 50-52 HRC
Medical Device Motor Shaft
Surgical Tool Motor Shaft

- Problem
A medical device company required miniature motor shafts for a new line of surgical tools. The application demanded extreme precision, biocompatibility, and complete freedom from micro-burrs that could compromise device function.
- Solution
Allied Metal utilized Swiss-style CNC turning machines with live tooling to produce the complex micro-features in a single setup. We implemented a proprietary deburring process that eliminated all micro-burrs without affecting critical dimensions.
±0.0001″
Concentricity Tolerance
0.4µm
Surface Finish (Ra)
100%
Cleanliness Validation
0
PPM Defect Rate
Material: 316L Stainless Steel, Passivated
Robotic Arm Drive Shaft
Precision Robot Drive Shaft
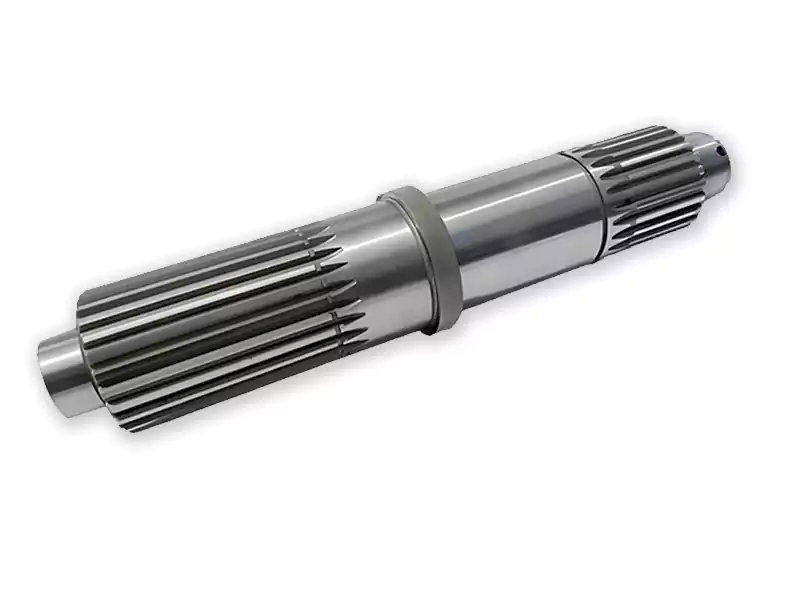

- Problem
A robotics manufacturer needed high-stiffness, lightweight drive shafts for a new collaborative robot arm. The design required complex spline features, precise balancing, and exceptional straightness to minimize vibration at high RPMs.
- Solution
Allied Metal employed 5-axis CNC milling with custom form tools to machine the complex spline geometry. We implemented a proprietary straightening process followed by dynamic balancing to meet the strict vibration requirements.
0.001″
Total Indicated Runout
0.5g·mm/kg
Balance Quality Grade
40%
Weight Reduction
15,000
RPM Operational Speed
Material: 7075-T6 Aluminum, Hard Anodized
FAQ
Please visit our CNC Machining FAQ page for additional common questions. Alternatively, contact us directly for details and a quote.
Ready to Manufacture Your Custom Shaft?
Our team of engineers is ready to review your design and provide a competitive quote with free DFM feedback. Let’s build your next high-performance component together.
