Coatings often fail when the wrong finishing method is selected, leading to corrosion, wear, and assembly issues that delay production and raise cost.
Powder coating is a dry finishing process that forms a durable, corrosion-resistant film through electrostatic powder application and heat curing, making it ideal for CNC-machined components used in industrial environments.
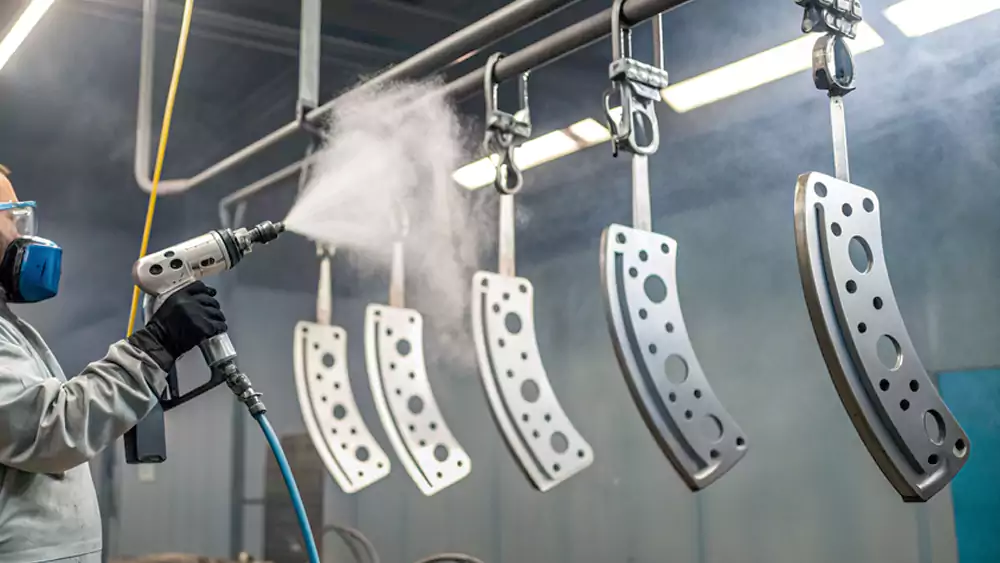

I want to walk you through powder coating from an engineering and procurement perspective. This guide explains how the process works, what factors matter most, and how to choose the right finish for CNC machined parts.
What Is Powder Coating?
Metal parts often fail in harsh environments when the coating cannot withstand vibration, moisture, or chemical exposure.
Powder coating is a solvent-free finishing method that melts powder resin onto metal, forming a thick, uniform, and highly durable surface that outperforms liquid paint in most industrial applications.
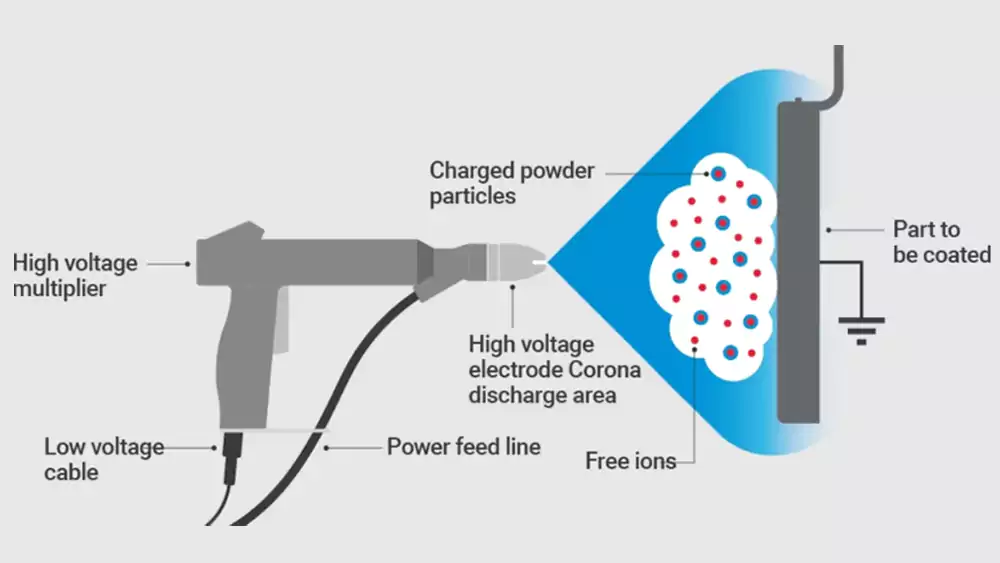
Powder coating is harder, thicker, and more consistent than wet paint and meets major environmental standards like EU RoHS and REACH1.
Key Characteristics
- Thickness: typically 60–120 μm
- Durability: strong abrasion and impact resistance
- Environmental stability: good UV and chemical resistance (depending on powder type)
- Appearance: available in smooth, matte, textured, and specialty finishes
- Environmental compliance2: low VOC, reclaimable powder reduces waste
- Material compatibility: suitable for aluminum, steel, stainless steel, magnesium
What This Means for Your Project
Powder coating is ideal when you need durability, consistent appearance, and protection against corrosion or wear. It hides minor machining marks and provides repeatable color and texture across batches—useful for components in automation, robotics, machinery covers, and safety frames.
How Does Powder Coating Work?
Coating problems rarely come from spraying—they usually start earlier with poor surface preparation or improper curing.
Powder coating works through cleaning, electrostatic application, and controlled heat curing, forming a permanent film that bonds tightly to the metal surface.
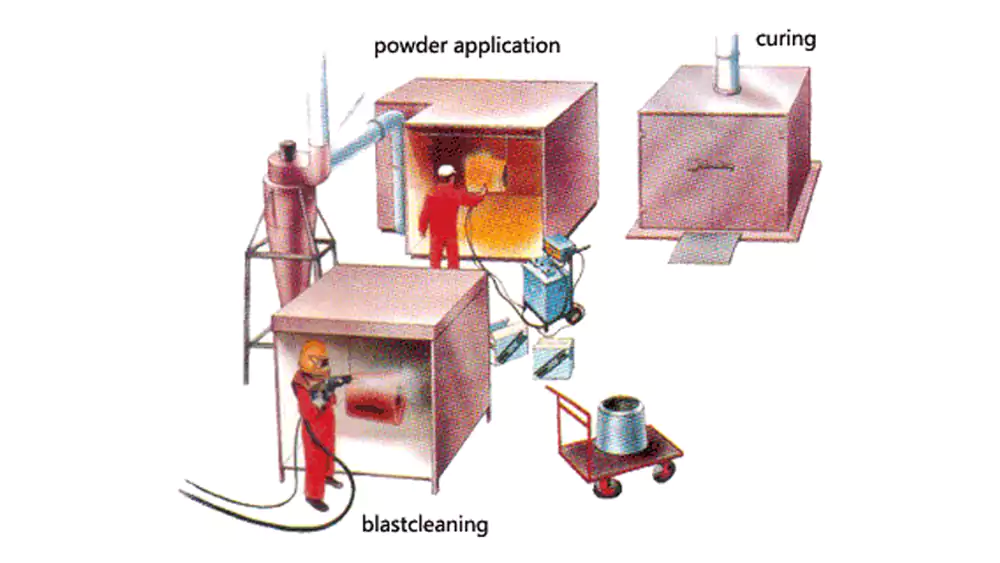
Each step affects adhesion, smoothness, thickness, and long-term durability.
Key Technical Factors to Consider
- Pretreatment: removes machining oil, coolant, oxidation, and fingerprints.
- Electrostatic spraying3: charged powder particles cling to grounded metal surfaces.
- Curing4: powder melts and cross-links at 160–220°C, forming a hard, durable film.
A small temperature deviation can cause significant surface issues. Years ago, a 10°C oven drift resulted in a full batch of brackets developing texture defects—ever since, I confirm oven calibration with every coater.
Benefits & Limitations in Industrial Use
Real-world performance—not datasheets—is what matters.
Powder coating offers high durability, corrosion resistance, UV stability, and long-term surface protection, but requires tolerance planning due to added thickness.
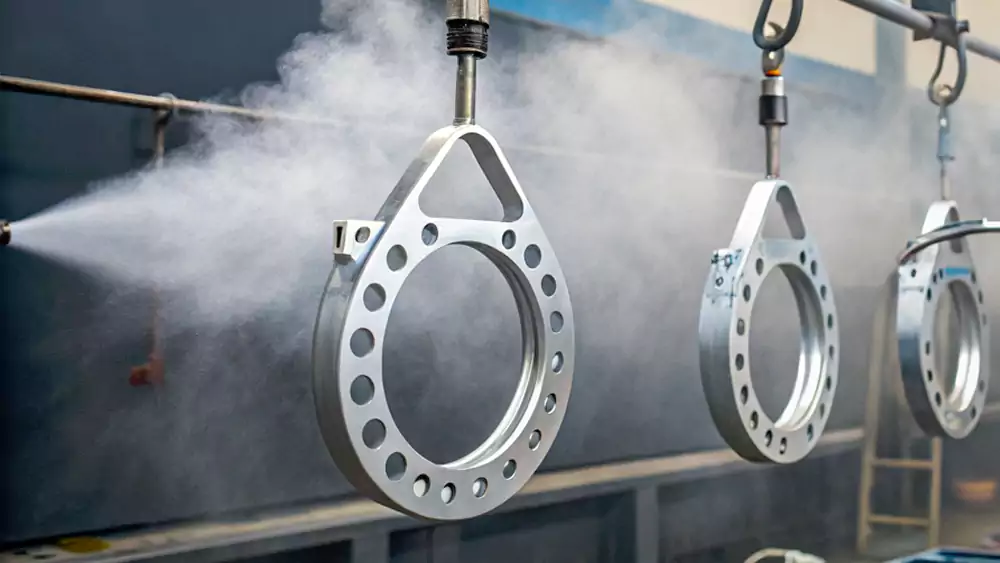

It is especially suitable for heavy-use parts exposed to vibration, impacts, or outdoor conditions.
What Buyers Must Confirm With Suppliers
- Powder chemistry selection (indoor vs outdoor)
- Target film thickness tolerance
- Masking areas and precision surfaces
- Pretreatment quality control and wash-line condition
- Oven curing consistency
- Color availability and RAL matching
Selecting the wrong powder type is a leading cause of early coating failure.
Choosing the Right Powder Type
Powder choice determines UV stability, chemical performance, impact resistance, and lifetime.
The main powder coating types—epoxy, polyester, hybrid, polyurethane, and specialty formulations—fit different environments and durability requirements.

Epoxy Powder Coating
Best for: indoor use
Strengths: excellent chemical resistance
Weaknesses: poor UV resistance
Polyester Powder Coating5
Best for: outdoor and industrial applications
Strengths: strong UV/weather resistance, good durability
Weaknesses: moderate chemical resistance
Epoxy-Polyester Hybrid
Best for: general indoor housings and enclosures
Strengths: balanced performance at a lower cost
Weaknesses: not suitable for outdoor exposure
Polyurethane Powder Coating
Best for: harsh industrial and chemical environments
Strengths: excellent mechanical durability and chemical resistance
Weaknesses: higher material cost
Specialty Low-Temperature Powders
Best for: thin-walled aluminum or temperature-sensitive components
Strengths: reduces risk of heat distortion
Weaknesses: limited color selection
Real-World Selection Advice for Engineers and Buyers
Outdoor components almost always need polyester.
Chemical environments require epoxy or polyurethane.
Thin aluminum parts benefit from low-temperature powders.
For most indoor applications, hybrids balance performance and cost.
Engineering Concerns: Materials, Tolerances & Masking
Powder coating is beneficial—but it can compromise precision if not planned early.
Powder coating adds 60–120 μm thickness and requires masking for threads, bores, and precision surfaces.
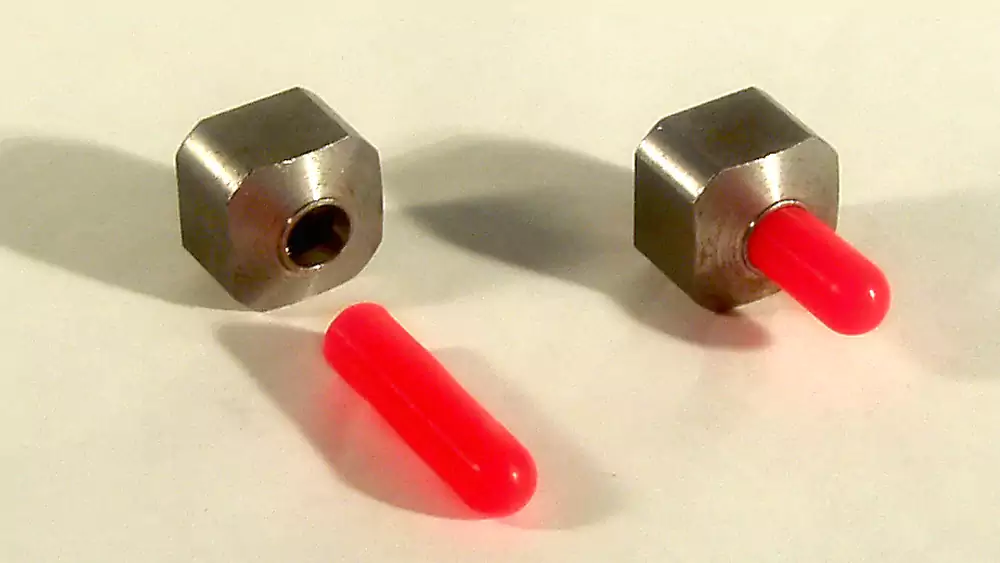
What Engineers Should Specify in Drawings
Material Considerations
- Aluminum: excellent adhesion with chromate pretreatment
- Steel: robust adhesion and corrosion resistance
- Stainless steel: requires surface roughening
- Magnesium: needs heat-sensitive powders
Tolerance Impact
Coating builds everywhere:
- Holes shrink
- External dimensions grow
- Sharp edges soften
- Threads must be masked
I often pre-adjust hole sizes or mark “MASK AREA” directly on the drawing.
Masking Requirements6
Masking ensures parts still assemble correctly. Suppliers use:
- Silicone plugs
- Heat-resistant tape
- Custom masking fixtures
Masking adds cost but prevents rework or rejected assemblies.
Quality Issues and Defect Prevention
Even experienced coaters can produce defects if controls are not strict.
Common powder coating defects include orange peel, pinholes, contamination, and adhesion failures—usually caused by poor pretreatment or incorrect curing.
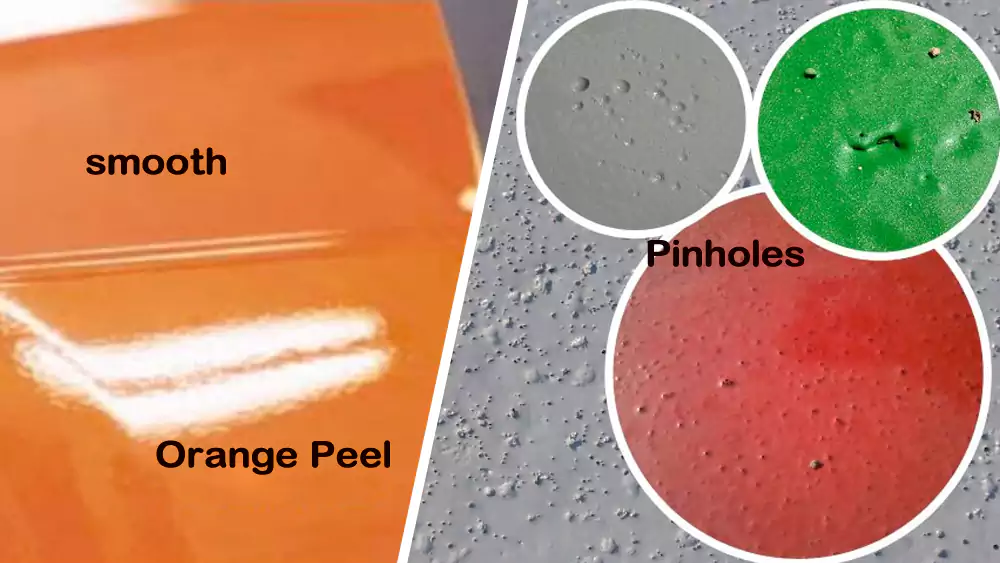

Risks to Avoid Early
- Orange peel → excessive thickness or improper cure
- Pinholes → oil, gas, moisture contamination
- Weak adhesion → insufficient pretreatment
- Runs → excess powder in corners or edges
A reliable coater maintains wash-line chemistry and runs daily test panels.
Powder Coating vs Other Finishing Methods
Not all projects require powder coating.
Here’s how it compares with anodizing and liquid painting.
Powder coating offers thick, durable protection, anodizing offers thin precision films, and painting offers lower cost but weaker durability.

Finish Comparison at a Glance
| Finish Type | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Coating | Strong durability, impact resistance, UV/weather protection | Adds thickness; requires masking | Industrial machinery, brackets, covers, frames |
| Anodizing | Thin, precise, excellent wear resistance (on aluminum) | Lower impact resistance; color limits | Precision aluminum parts, consumer products |
| Liquid Painting | Low cost, flexible colors, simple process | Chips more easily; poor UV/chemical resistance | Low-volume runs, prototypes, cosmetic parts |
This table helps teams quickly determine the best finishing method for CNC machined components.
Case Study: Powder Coating CNC Aluminum Brackets
A customer in the automation industry requested CNC-machined 6061-T6 aluminum brackets requiring a durable black finish and strict dimensional accuracy for a sliding assembly.
1. Customer Requirements
- Material: 6061-T6 aluminum
- Critical Feature: Ø28 mm bore, tolerance ±0.05 mm
- Finish: RAL 9005 matte black powder coating7
- Environment: light outdoor exposure + vibration load
- Batch Size: 300 pcs per order
- Durability Need: no chipping after 1M motion cycles
2. Engineering Challenges
- Bore tolerance could not accept 60–120 μm coating buildup
- Part included two flat mounting surfaces that required smooth contact
- Thin wall area (2.2 mm) risked deformation under curing temperature
- customer required minimal color variance across batches
3. Process Setup & Specification
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Pretreatment | Chromate conversion (Aluminum) |
| Powder Type | Polyester (outdoor-rated) |
| Color | RAL 9005 Matte |
| Target Thickness | 80 μm |
| Curing Profile | 185°C × 18 minutes |
| Masking | Precision bore + mounting faces |
| Measured Film Thickness | 76–84 μm |
| Dimensional Change | +0.08 mm on unmasked edges |
| Tolerance Control | Bore remained within ±0.02 mm after masking |
4. Final Results
- Zero rework across 300 pcs
- Bore remained fully within tolerance due to effective masking
- No warping even with thin walls, thanks to controlled curing
- Uniform color across all batches
- Passed 1 million vibration cycles without peeling or cracking
- Customer approved the setup as their long-term production standard
Why This Case Matters
This case clearly demonstrates how powder type, thickness control, masking quality, and curing accuracy directly affect dimensional stability and long-term durability. For procurement teams, it highlights what to evaluate when selecting a reliable finishing supplier.
Conclusion
Powder coating delivers long-term protection for CNC-machined parts when engineers and buyers plan early for powder chemistry, thickness impact, and masking requirements. Strong performance comes from coordination between machining and finishing—not from coating alone. With the right preparation and supplier alignment, powder coating becomes a dependable and cost-effective finishing choice for industrial applications.
-
Learn about these important environmental standards to understand their impact on manufacturing and product safety. ↩
-
Exploring environmental compliance in powder coating can guide you in selecting eco-friendly options that meet regulations and reduce waste. ↩
-
Understanding electrostatic spraying can enhance your knowledge of coating processes and improve application techniques. ↩
-
Exploring the curing process will provide insights into achieving optimal durability and finish in powder coating applications. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand why Polyester Powder Coating is ideal for outdoor use, offering strong UV resistance and durability. ↩
-
Understanding masking requirements is crucial for ensuring proper assembly and avoiding costly rework. ↩
-
Explore the advantages of RAL 9005 matte black powder coating for durability and aesthetics in outdoor applications. ↩

