CNC machining vs 3D printing: The Expert's Guide to Choosing Right
- November 29, 2024
- Tony
- Last updated on October 29, 2025 by Lucy
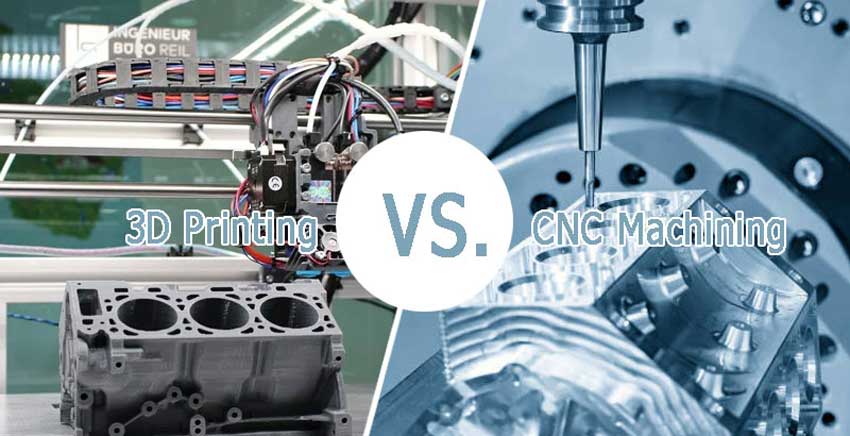
CNC machining and 3D printing differ fundamentally: CNC machining is a subtractive process, while 3D printing is additive. This article compares both methods to help you select the best one for your project.
1. CNC Machining: The Precision Workhorse
1. What is CNC machining?

CNC machining is like digital sculpting – we start with a solid block and remove everything that doesn’t look like your part. It’s subtractive manufacturing at its finest.
2. Common CNC Machining Methods
3. Advantages and Limitations of CNC Machining
- Precision & Repeatability: Ensures high accuracy and consistency, ideal for complex, high-precision parts with minimal errors.
- Excellent Surface Quality: Produces smooth surfaces, reducing the need for additional finishing, perfect for parts with high aesthetic demands.
- Efficient Production: Once programmed, CNC machines run automatically, enabling stable, high-volume production and reduced labor costs.
- Versatile Capability: Can process complex shapes and fine details, making it ideal for modern, intricate designs.
- High Initial Cost: CNC equipment is expensive, making it better suited for mass production or long-term projects.
- Setup Time: Initial setup and programming take time, leading to longer lead times for urgent orders.
- Best for Mass Production: CNC machining is most cost-effective for large batches, less so for small runs or one-off custom parts.
2. 3D Printing: The Speed Demon
1. What is 3D printing?

3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process that creates three-dimensional objects by layering materials. Unlike traditional methods, it builds parts directly from computer designs using spraying, extrusion, or light-curing techniques.
2. Common 3D printing technologies
Common 3D printing technologies include FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), SLA (Stereolithography), and SLS (Selective Laser Sintering):
- FDM is cost-effective and fast, ideal for durable parts using thermoplastics.
- SLA offers high precision and smooth finishes, perfect for detailed prototypes.
- SLS fuses powdered materials with lasers, providing strong, functional parts with complex geometries.
3. Advantages and Limitations of 3D Printing
- Fast Prototyping & Customization: Ideal for quickly creating complex prototypes and small-batch custom designs.
- Design Flexibility: Enables the production of intricate shapes that are hard to achieve with traditional methods.
- Surface Quality & Precision: May not offer the same surface finish or accuracy as traditional machining.
- Material Limitations: Fewer material options with potentially lower performance compared to CNC machining.
3. CNC Machining vs 3D Printing
1. CNC machining and 3D printing similarities
- Automation and Precision: Both CNC machining and 3D printing are computer-controlled, ensuring efficient, precise production with minimal human error.
- Material Suitability: Both technologies support a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, for different parts.
- Application Scope: Both can produce complex parts. CNC is ideal for high-precision, high-strength components, while 3D printing excels at creating intricate structures.
- Design Freedom: Both methods allow for complex designs—CNC removes material, while 3D printing builds objects layer by layer.
2. Key Comparison Factors
Comparison Factors | CNC Machining | 3D Printing |
Accuracy & Surface Quality | Superior accuracy and surface finish, ideal for tight tolerances | Requires post-processing to achieve similar quality |
Material Selection | Works with a wide range of materials, consistent strength | Limited materials, may not meet strength requirements |
Production Speed | More setup time, efficient for large-scale production | Faster for small batches and prototypes with minimal setup |
Cost-Effectiveness | More cost-effective for large-volume production | More economical for small runs and custom parts |
Part Complexity | Can handle complex shapes, but may need extra steps/tools | Excels at complex geometries and intricate designs |
Strength & Durability | Produces stronger, more durable parts, especially with metals | Less durable, better suited for prototyping unless specialized materials are used |
📌Case Study: Aerospace Bracket - Hybrid Approach Saves $15,000
We had a client designing a complex mounting bracket for satellite equipment. Their initial approach was traditional CNC machining, but the costs were staggering.
The Challenge:
- Original CNC quote: $22,000 for 5 prototypes
- 8-week delivery timeline
- 85% material waste in titanium
- Complex internal cooling channels impossible with CNC
Our Hybrid Solution:
- Step 1: 3D print the main body with internal channels using DMLS titanium
- Step 2: CNC machine the critical mounting surfaces and threads
- Step 3: Heat treat and stress relieve
Results:
- 3D printing time: 28 hours
- CNC machining time: 3 hours per part
- Material usage: 15% waste (vs 85% with full CNC)
- Total cost: $7,200 (67% savings)
- Delivery: 3 weeks (57% faster)
- Strength: 98% of wrought material properties
The client got flight-ready prototypes in half the time for one-third the cost. Sometimes the best solution uses both technologies.
4. When to choose CNC machining?

1. High precision and complex parts
This method is ideal for parts that require tight dimensional tolerances and excellent surface finishes. It delivers exceptional precision, making it perfect for complex components with high-detail requirements, such as those in aerospace, medical devices, and other critical industries.
2. High-Volume Production
While initial setup takes time, this technology is highly efficient for large-scale production. Its automation and ability to quickly switch between different programs make it perfect for environments that demand high throughput and repetitive tasks.
3. Machining Hard Materials
For materials with high hardness or durability demands (such as steel, aluminum alloys, or titanium), CNC machines provide significant advantages.
4. Complex Part Manufacturing
When a part design involves multiple steps (like milling, drilling, and turning), CNC machines can handle multiple processes in one go, minimizing the need for part transfers and manual interventions, thus improving overall efficiency.
5. Customization and Mass Production
CNC machine processing are ideal for both custom parts and mass production. Even for one-off items, they can precisely follow design specifications, ensuring consistency and high quality. For large runs, they also offer cost efficiency.
5. When to choose 3D printing?
3D printing is a fast and flexible technology that excels in the following situations:

1. Rapid Prototyping
When there’s a need to quickly validate design concepts or conduct functional testing, 3D printing helps speed up the product development process by producing prototypes quickly and affordably.
2. Small Batch Production
For small batch runs, this technology offers clear advantages. Without the need for molds, it enables fast production of personalized or customized parts, ideal for short-term projects or bespoke products.
3. Complex Designs
Complex geometries and internal structures that are difficult to achieve with conventional methods can be handled. It’s particularly suited for parts with complex shapes, such as custom medical implants or specialized consumer electronics housings.
4. Speed Over Everything
Need it yesterday? 3D printing can often deliver in hours.
6. The Smart Combo: Using Both Technologies
In modern manufacturing, combining CNC machining and 3D printing is an efficient production method. For example, in automotive engine components, 3D printing is used to create complex internal structures, which are then CNC machined for improved accuracy and quality.

Each technology has its strengths, and using them together maximizes efficiency and precision, especially for complex parts, while reducing costs and production time.
7. FAQs
“Which is stronger – CNC or 3D printed?”
CNC, every time. You’re working with proven material properties, not layer-bonded material.
“When does CNC become cheaper than 3D printing?”
Usually around 10-20 parts, depending on complexity.
“Can I get the same surface finish with 3D printing?”
Not even close. The best 3D printed parts still need post-processing to match CNC finishes.
“What about material options?”
CNC: Thousands. 3D printing: Dozens.
Still have questions? Browse our complete FAQs page to find what you’re looking for.
8. Conclusion
When deciding between CNC machining and 3D printing, it all comes down to your project’s needs.
- If you’re looking for high-volume production with parts that need to be precise and strong, CNC machining is the way to go.
- On the other hand, if you need fast prototyping, small batch production, or custom parts with complex shapes, 3D printing offers more flexibility and is often more cost-effective.
Ultimately, by considering factors like project scale, budget, accuracy, and material requirements, you can choose the right method to boost both efficiency and product quality.
