Overview
1. What is CNC fixturing?
A CNC fixture is a specialized tool used to hold and support a workpiece for machining on a CNC machine. It ensures the stability and accuracy of the workpiece during machining by precise clamping.
2. What are CNC fixtures?
CNC fixtures mainly include standard fixtures, special fixtures and intelligent fixtures. Different types of fixtures are suitable for different machining needs and workpiece shapes.
Application of CNC fixtures
In CNC machining, CNC fixture plays a vital role. It not only improves the machining accuracy, but also shortens the machining time.
In different processes such as turning , milling, drilling, etc., the application of CNC fixtures is able to realize more efficient automated machining, reduce manual intervention and lower the error rate.
The main components of CNC fixtures
CNC fixtures are usually composed of parts such as clamping mechanism, positioning device, support structure and adjustment mechanism. Each part plays an important role in the overall function of the fixture.
Common types of CNC fixtures
1. According to the CNC machining mode classification
Turning fixtures
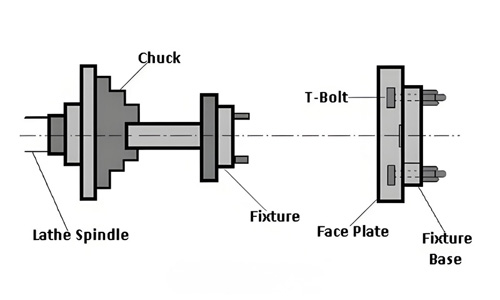
Used to hold rotating workpieces and ensure the stability of the cutting tool.
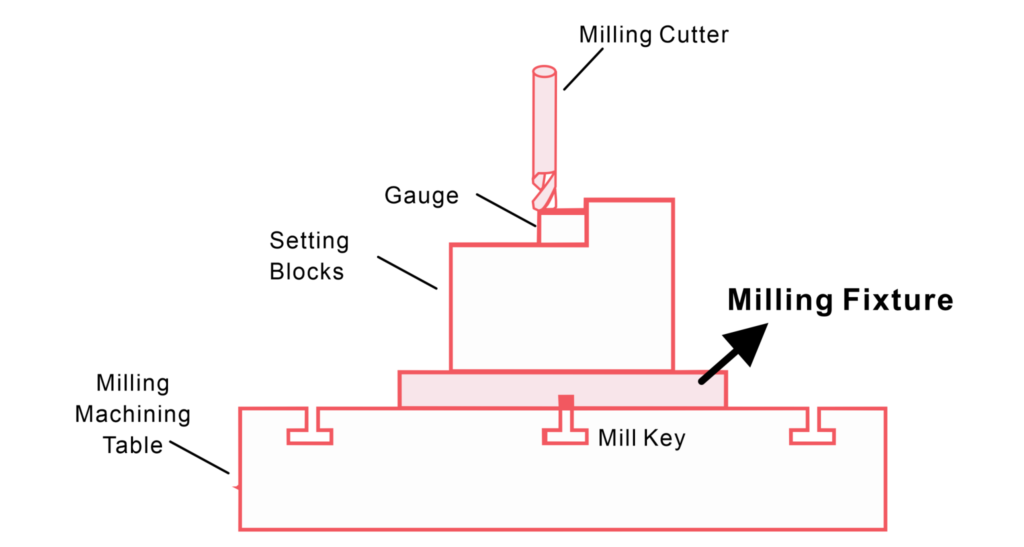
Milling fixture
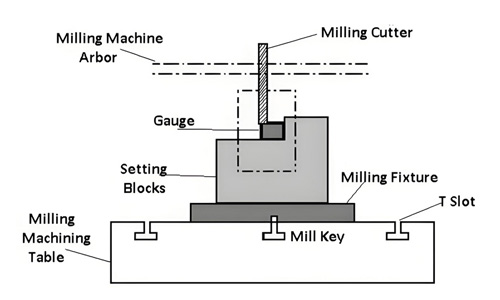
Used for milling workpiece, usually with multi-directional clamping capacity.
Drilling fixtures

Designed for drilling to ensure accurate positioning of the drill.
Grinding Fixtures
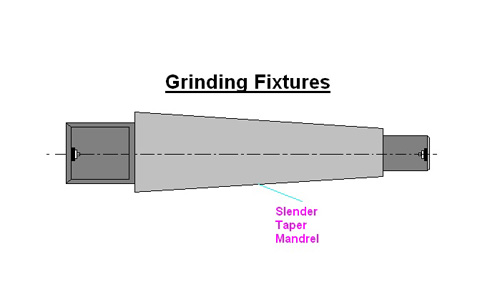
Used in the grinding process to provide good stability of the workpiece.
Boring fixtures
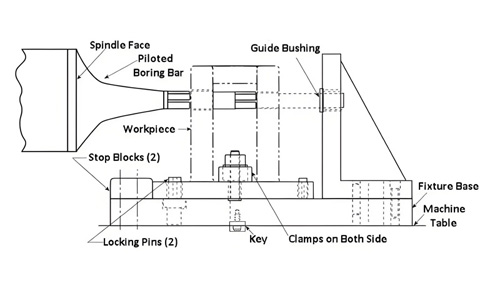
Specially designed for boring process to ensure the accuracy of holes.
2. Classification according to use
General purpose fixtures
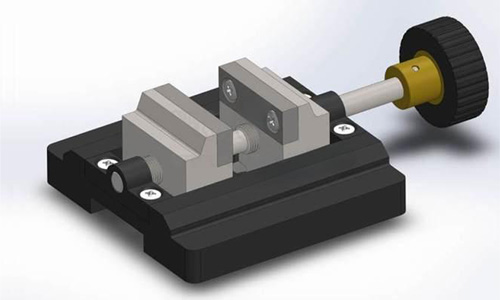
These fixtures have been standardized and are suitable for a wide range of workpieces, such as three-jaw chucks, flat vise and magnetic workbench. General-purpose fixtures are adaptable and can handle workpieces of certain shapes and sizes, but with lower precision, suitable for small batch production, and difficult to clamp workpieces of complex shapes.
Specialized fixture
Designed for a specific process of a certain workpiece. They can improve efficiency and accuracy in stable mass production, but the design and investment costs are higher, usually used in mass production, may also be used in small and medium-sized mass production.
Adjustable fixtures
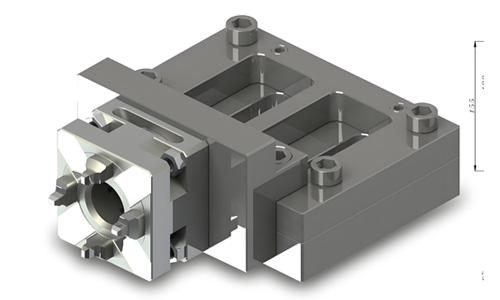
Some elements of these fixtures can be adjusted or replaced to accommodate a wide range of workpieces to be machined. Adjustable fixtures overcome the shortcomings of universal and specialized fixtures and are divided into universal adjustable fixtures and grouped fixtures, the latter being suitable for small to medium volume production.
Combined fixture
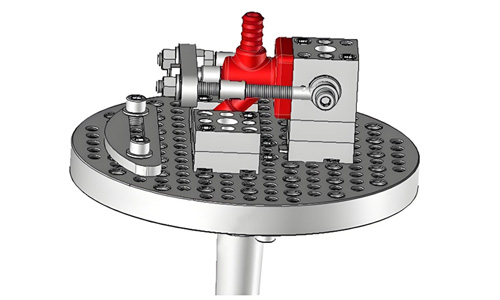
Assembled from standardized modular components, designed for a particular workpiece process. Combined fixtures are highly accurate, wear-resistant, and suitable for small-lot production or small and medium-sized workpieces.
Traveling Fixture
These fixtures move with the workpiece and are suitable for automated production lines to ensure positioning and clamping of the workpiece during machining.
3. Classification according to power source
CNC fixtures can be categorized according to the source of power, which mainly includes the following:
- Manual fixtures
- Pneumatic fixtures
- Hydraulic fixtures
- Electrical fixtures
- Electromagnetic fixtures
- Vacuum clamps
The selection and use of these CNC fixtures depends on the specific machining requirements, workpiece characteristics and production environment.
Difference between CNC fixtures and traditional fixtures
CNC fixtures and traditional fixtures mainly differ in automation and precision. Here’s a breakdown:
- Automation & speed: CNC fixtures support fast, automated clamping and releasing. This reduces manual steps and speeds up setup under computer control. Traditional fixtures, in contrast, often require more manual intervention and take more time.
- Accuracy & consistency: With CNC fixtures, you get more stable and repeatable positioning across multiple parts. The precision is high and consistent throughout the production run. Traditional fixtures may offer acceptable accuracy, but they’re more prone to variation between parts.
- Adaptability & flexibility: CNC fixtures can be designed (or even programmed) to accommodate different workpiece geometries and changes in production. Traditional fixtures tend to be more rigid in their design and better suited for simpler or repeated tasks.
- Efficiency in high volume or complex machining: In complex or high-volume operations, CNC fixtures show their advantages — less downtime, fewer errors, and better throughput. Traditional fixtures may still work well for small batches or simpler shapes, but their limitations become apparent under more demanding conditions.
Installation of CNC fixture
When installing a CNC fixture, you need to ensure that it fits precisely with the machine tool and the workpiece.

First, check the parts of the fixture to make sure there is no damage;
Secondly, install the fixture firmly on the machine tool;
Finally, carry out the positioning and clamping adjustment of the workpiece.
Analysis of common problems of CNC fixtures
Check the positioning accuracy and clamping strength of the fixture and adjust if necessary.
Regularly check and replace worn parts to keep the fixture in the best condition.
Select according to the shape of workpiece, machining process and accuracy requirements.
Clean, lubricate and check all parts for wear regularly.
Ensure that the design of the fixture matches the characteristics of the workpiece and customize it if necessary.
Summary
Understanding CNC fixtures is essential for procurement managers seeking high-quality, efficient CNC machining solutions. These fixtures directly influence machining accuracy, production speed, and cost-effectiveness. By knowing the different types of fixtures, their functions, and how they compare to traditional setups, buyers can make smarter sourcing decisions, ensure consistent part quality, and partner more effectively with machining suppliers.
