CNC machines often fail not because of cutting paths, but because auxiliary actions are misunderstood. I have seen good parts ruined by small command mistakes that people overlook.
M-code is the command language that controls non-cutting actions in CNC machines, such as spindle start, coolant flow, and tool change. Understanding it is essential for stable, repeatable, and safe machining operations.

I have worked with CNC machines for more than twenty years. In that time, I learned that most production problems do not come from geometry, but from how the machine is told to behave. That is where M-code quietly controls everything in the background.
What Is M-Code and How Does It Function in CNC Machines?
M-code problems often appear late in production. When they show up, they cost time, scrap, and trust. Many engineers know G-code well but treat M-code as an afterthought.
M-code is a set of commands that control machine functions rather than tool movement, working together with G-code to execute a complete machining cycle.

What M-code controls in real machining
M-codes manage actions that do not directly remove material. These actions still decide whether a part is produced safely and consistently.
Typical functions include:
- Spindle start and stop
- Coolant on and off
- Tool change execution
- Program stop or end
- Chuck clamp and unclamp on lathes
In my shop, I always say that G-code draws the path, but M-code keeps the machine alive. Without correct M-code logic, even a perfect toolpath will fail.
How M-code works together with G-code
M-codes are executed line by line inside a CNC program. They trigger physical actions on the machine while G-code defines motion.
For example, the machine will not cut unless:
- The spindle is running at the correct speed
- The tool is fully clamped
- The coolant is active when needed
This cooperation is why experienced machinists always review M-codes before pressing cycle start.
The Structure, Syntax, and Common Types of M-Codes?
Many errors come from assuming M-codes are universal. They are not. Understanding their structure is the first step to using them safely.
An M-code usually starts with the letter “M” followed by a number that triggers a specific machine action, though meanings can vary by machine and control system.

Basic structure of an M-code command
A simple M-code looks short, but its effect can be large.
Example format:
- M03 → Spindle on, clockwise
- M05 → Spindle stop
- M08 → Coolant on
- M09 → Coolant off
These commands are short by design. CNC controls1 must read them fast and without ambiguity.
Common categories of M-codes
Over the years, I group M-codes into practical categories when training new staff.
| Category | Typical Function |
|---|---|
| Spindle control2 | Start, stop, direction |
| Coolant control | Flood, mist, off |
| Tool control | Tool change, tool clamp |
| Program flow | Stop, optional stop, end |
| Fixture control | Chuck or clamp actions |
This grouping helps engineers understand intent instead of memorizing numbers.
Standard vs machine-specific M-codes
Some M-codes are widely shared. Others are defined by the machine builder.
For example:
- M03 and M05 are almost universal
- Custom M-codes may control probes, robots, or pallet systems
This difference becomes critical when outsourcing machining across regions or suppliers.
M-Codes Across Machines and CNC Control Systems?
Many sourcing problems appear when programs move between machines. Engineers expect the same result, but the machine reacts differently.
M-codes are not fully standardized and can behave differently across CNC controllers such as Fanuc, Siemens, and Haas.
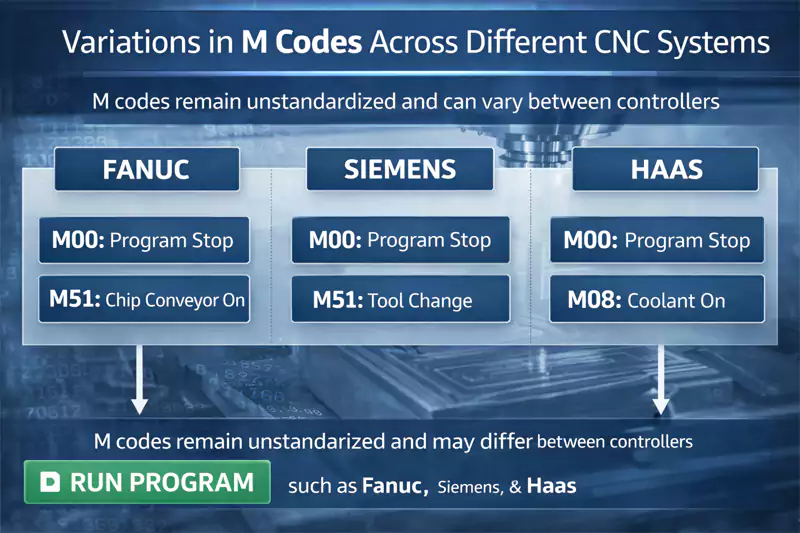
Differences between common control systems
In daily production, I often see these patterns:
| Control System | Typical Behavior |
|---|---|
| Fanuc3 | Stable standard M-codes, flexible customization |
| Siemens4 | Strong logic integration, more parameters |
| Haas5 | User-friendly, some unique M-code definitions |
Even when the M-code number is the same, the timing or conditions may differ.
Why this matters in outsourced machining
When a European engineer sends a program to a Chinese factory, assumptions can break.
Common risks include:
- Coolant timing differences
- Tool change confirmation delays
- Optional stop behavior mismatch
At Allied Metal, we always review customer programs and rewrite M-code sections when needed. This step prevents surprises on the shop floor.
Practical Applications, Risks, and Safety Considerations?
M-codes show their true value in real production, not in textbooks. They also carry the highest risk when used incorrectly.
Correct M-code logic ensures safe operation, while incorrect usage can cause crashes, scrap, and machine damage.

Real-world case study from my shop
Several years ago, we produced custom aluminum housings for an industrial automation client.
Project parameters
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum 6061-T66 |
| Machine | 3-axis vertical machining center |
| Control | Fanuc |
| Batch size | 500 units |
| Tolerance | ±0.02 mm |
| Cycle time | 6.5 minutes per part |
Issue
The original program used M08 coolant activation too late in the cycle.
Result
- Tool temperature increased
- Surface finish degraded after 120 parts
- Tool life dropped by 30%
Correction
We adjusted the M-code sequence to activate coolant before tool engagement.
Outcome
- Stable surface finish
- Full batch completed without tool failure
This small M-code change saved both time and cost.
Common M-code mistakes
From my experience, these mistakes appear often:
- Forgetting to stop the spindle before tool change
- Using optional stops incorrectly in production runs
- Assuming fixture M-codes are the same across machines
Each one can shut down production in seconds.
Safety considerations
M-codes often control safety-related actions7. This is why we test them carefully before mass production.
A single wrong clamp command can damage a fixture or injure an operator.
M-Code vs G-Code and Who Needs to Understand Them?
Many people ask if they really need to understand M-codes when outsourcing machining. The answer depends on their role.
G-code defines motion, while M-code controls machine behavior, and both are essential for predictable CNC production.
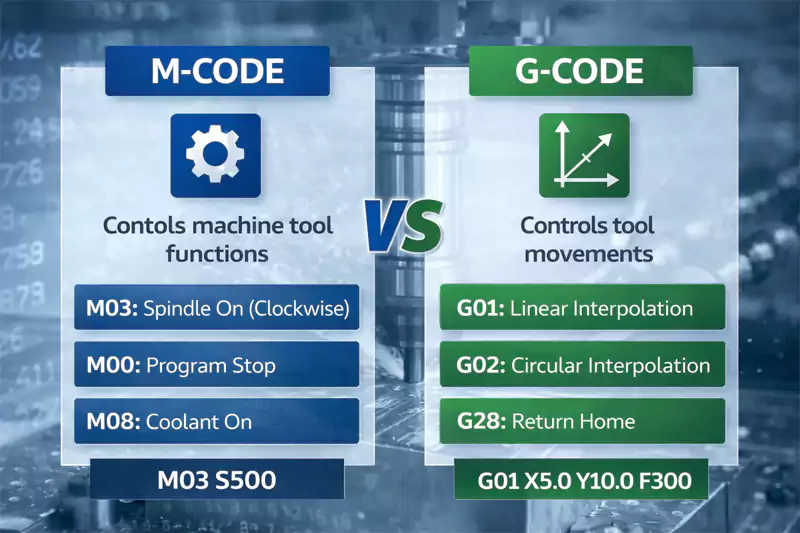
Key functional differences
| Aspect | G-Code | M-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Tool movement | Machine actions |
| Focus | Geometry | Behavior |
| Visibility | CAD/CAM output | Often manual or edited |
| Risk | Dimensional error | Safety and process failure |
Who really needs to know M-code
Design engineers do not need to write M-codes. Procurement managers do not need to memorize them. But both should understand their impact.
When sourcing custom CNC parts, knowing how a supplier manages M-codes helps you judge:
- Process maturity
- Risk control
- Production stability
This understanding builds trust between buyer and manufacturer.
Conclusion
M-code may look simple, but it controls the most critical machine actions. In my experience, mastering it is key to safe, consistent, and scalable CNC machining.
-
Exploring CNC controls will deepen your knowledge of how machines execute commands, improving your programming efficiency. ↩
-
Exploring spindle control will enhance your knowledge of machine operations and improve your CNC skills. ↩
-
Understanding Fanuc Control Systems. CNC controllers for reliable, high-performance CNC systems. ↩
-
Learn more about the Siemens control system product range. ↩
-
Fast, smart, and powerful, the Haas CNC control offers a simple, intuitive interface that’s easy to learn and use. ↩
-
Understanding Aluminum 6061-T6's properties can enhance your material selection for projects, ensuring optimal performance. ↩
-
Learn about the importance of safety-related actions in CNC machining to prevent accidents and ensure smooth operations. ↩

