Table of Contents:
CNC Machining in the Medical Industry: Precision That Saves Lives
- October 31, 2024
- Tony
- Last updated on October 31, 2025 by Lucy
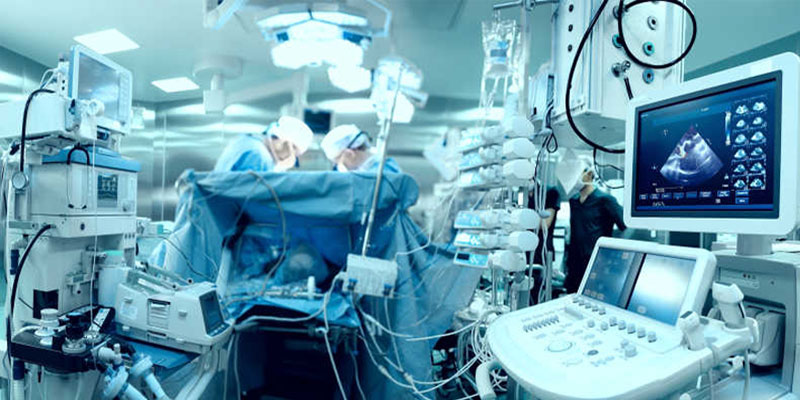
Medical parts aren’t just components – they’re lifelines. Every implant, surgical tool, or diagnostic device we make could end up inside someone’s body. That’s why we treat every job with the seriousness it deserves.
1. CNC machining in the medical industry
CNC machining (CNC) technology is playing an increasingly important role in the medical industry. As medical devices and equipment require increasing precision and reliability, CNC machining provides a powerful solution to meet these needs.
2. Why is CNC machining suitable for the medical industry?
CNC machining in the medical industry offers the advantages of high precision and repeatability to meet stringent medical regulations and standards. In addition, the flexibility of CNC machining allows for much greater customization and the ability to respond quickly to market needs.
It's About More Than Just Measurements
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
- Tolerances matter: We regularly hold ±0.005mm on critical implant features
- Surface finish is crucial: Ra 0.2μm or better for parts that contact tissue
- Material traceability: Every batch comes with full certification and lot tracking
What Makes CNC Perfect for Medical
- Consistency: Part 1 matches part 10,000 exactly – no surprises in the OR
- Complex geometries: We machine shapes that would be impossible with conventional methods
- Material versatility: From titanium implants to PEEK surgical guides
3. The Importance of Precision in Medical Devices.

The accuracy of medical devices is crucial in the following ways:
Patient safety: Highly accurate medical devices protect patients by ensuring the accuracy of procedures and treatments and reducing the risk of medical errors.
Therapeutic efficacy: Accurate device design and manufacturing can improve the effectiveness of treatments and ensure that medical procedures achieve the desired results.
Regulatory Compliance: Medical devices are subject to strict industry standards and regulations, and high-precision manufacturing processes help meet these requirements and avoid legal risks.
Device Reliability: High-precision manufacturing improves the reliability of devices and reduces the need for malfunctions and maintenance, thus enhancing the continuity and stability of healthcare services.
To summarize, the precision of medical devices directly affects patient safety, therapeutic efficacy, and the overall reliability of the device, and therefore must be given high priority during the design and production process.
4. What are the common CNC machining methods used in the medical field?
The following are common CNC machining methods and their characteristics:

Cnc Turning
Primarily for symmetrical parts, such as needles and tubes, turning ensures high precision and excellent surface finish.

Cnc Milling
Used for creating complex shapes in medical components, allowing precise control over the cutting process.

laser Cutting
Offers high precision and clean edges, suitable for thin materials in medical packaging and devices.

3D Printing & CNC
Enhances customization and flexibility, meeting the diverse needs of personalized medical devices.
5. CNC machining in the medical industry.
Surgical instruments

Examples include scalpels, forceps, etc., which require high precision and durability.
Medical equipment
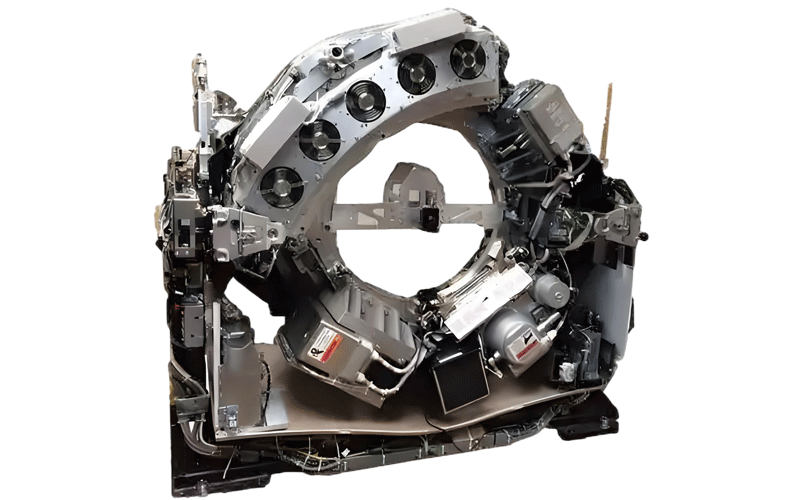
For example: CT scanner, X-ray machine components, need to ensure the stability and reliability of the equipment.
Customized implants
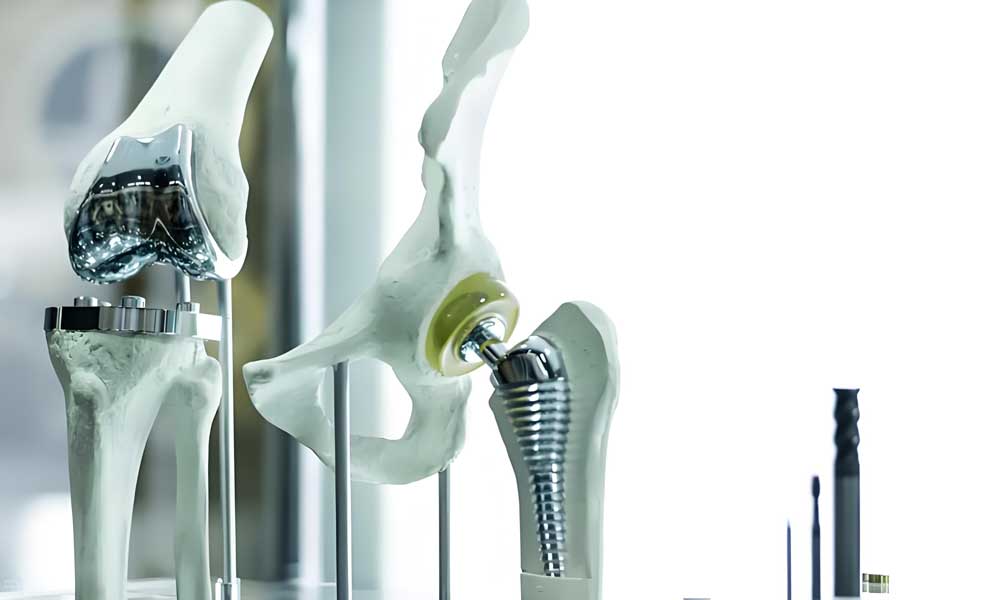
Examples: Artificial joints, dental implants, personalized according to patient’s needs.
Prosthetics and orthotics
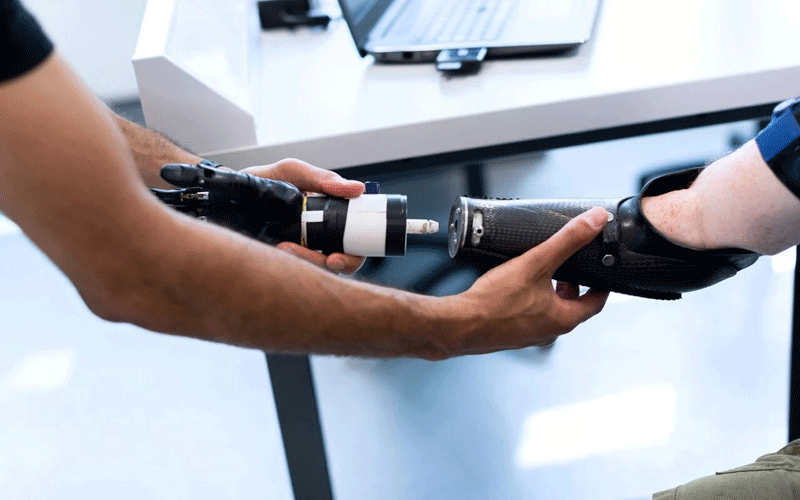
Personalized design and fabrication to suit the specific needs of the patient.
Microdevices
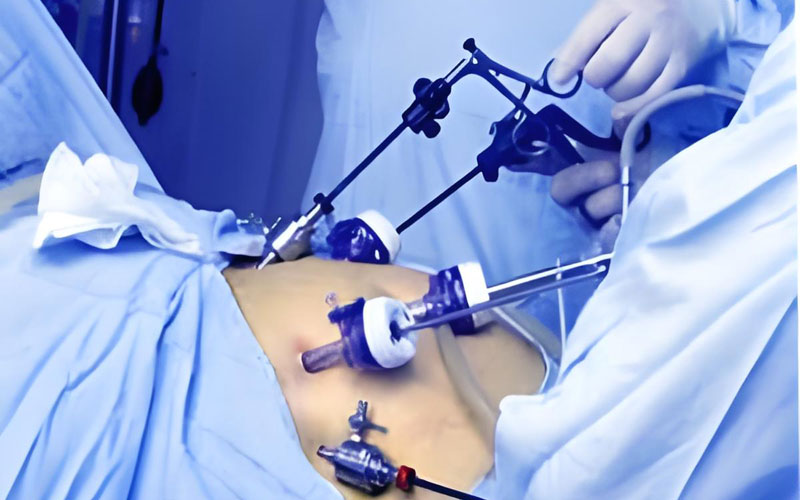
High precision devices for minimally invasive surgery.
Rehabilitation and assistive devices
Customized parts to meet the needs of walkers, wheelchairs, and other equipment to improve user comfort and convenience.
Medical teaching aids
Application tools for teaching and training to help medical personnel better master their skills.
📌Case Study: Titanium Spinal Fusion Cage
The Challenge: A medical device startup needed 5,000 titanium spinal cages for minimally invasive surgery. The part had to be strong enough to support spinal loads while allowing bone growth through precisely sized openings.
Our Solution: We set up dedicated 5-axis CNC cells with integrated CMM verification after every 50 parts.
Production Details:
- Material: Ti-6Al-4V ELI (medical grade)
- Critical Features: 0.8mm wall thickness with ±0.01mm consistency
- Surface Finish: Ra 0.4μm on all bone-contact surfaces
- Porosity: Machined openings sized 0.5-2.0mm for optimal bone integration
- Sterilization: Passed all validation for gamma and EtO methods
- Documentation: Full DHR with traceability to material melt lots
- Volume: 500 units monthly with 4-week lead time
The tricky part was maintaining the thin walls while achieving the required surface finish. We ended up developing custom tool paths that used trochoidal milling to reduce tool pressure and prevent part deflection.
6. Materials We Trust for Medical Applications
Material Type | Material | Properties | Applications |
Metals | Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, high strength, easy to clean | Surgical instruments, implants |
Titanium Alloy | Lightweight, high strength, biocompatible | Artificial joints, dental implants | |
Nitinol | Shape memory properties, excellent biocompatibility | Prosthetics, orthotics | |
Copper Alloy | Excellent conductivity and antimicrobial properties | Electrical connectors, medical device components | |
Plastics | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) | High strength, high temperature resistance, good biocompatibility | Medical implants, instrument parts |
Polyurethane | Good elasticity, wear resistance | Prosthetics, orthotics | |
Polycarbonate | Excellent transparency, impact resistance | Medical device displays, shields | |
Other Materials | Carbon Fiber Composites | Lightweight, high strength, corrosion-resistant | Rehabilitation equipment, supports |
Bioceramics | Excellent biocompatibility and mechanical properties | Dental implants, bone substitutes | |
Silicone | Excellent flexibility and biocompatibility | Medical teaching tools, protective gear | |
Polymer Gel | Good elasticity, comfort | Prosthetic liners, orthotic liners | |
3D Printing Materials | Highly customizable and flexible | Custom medical devices, models | |
Synthetic Resin | High strength, good machinability | Casings and parts for medical equipment |
7. The Medical Manufacturing Mindset
Quality Isn’t Just a Department – It’s Everyone’s Job
- First Article Inspection: Every new part gets measured 50+ ways before production
- In-process checks: We verify critical dimensions every 2 hours
- Final validation: Every part gets a final look before clean room packaging
Documentation That Would Make the FDA Smile
- Material certs: We keep records for 10+ years
- Process validation: We prove our methods work before making your parts
- Device History Records: Complete traceability from raw material to finished part
8. Why Medical Manufacturing Is Different?
It’s Personal
I’ve met surgeons who use tools we’ve made. I’ve seen X-rays of our implants in patients. This isn’t just metal and plastic – it’s people’s quality of life.
The Stakes Are Higher
A failed automotive part might mean a tow truck. A failed medical device could mean a second surgery. We never forget that.
9. Looking Ahead: Where Medical CNC Is Headed?
The Future Is Already Here
- Patient-specific implants: Custom parts from patient CT scans
- Combined technologies: 3D printing rough shapes, CNC finishing critical features
- Smart manufacturing: Real-time quality monitoring that predicts issues before they happen
CNC machining plays a key role in the medical industry, and its application will continue to expand with the advancement of technology and changes in market demand. We should pay attention to the development of this field to promote higher quality medical devices and services.
