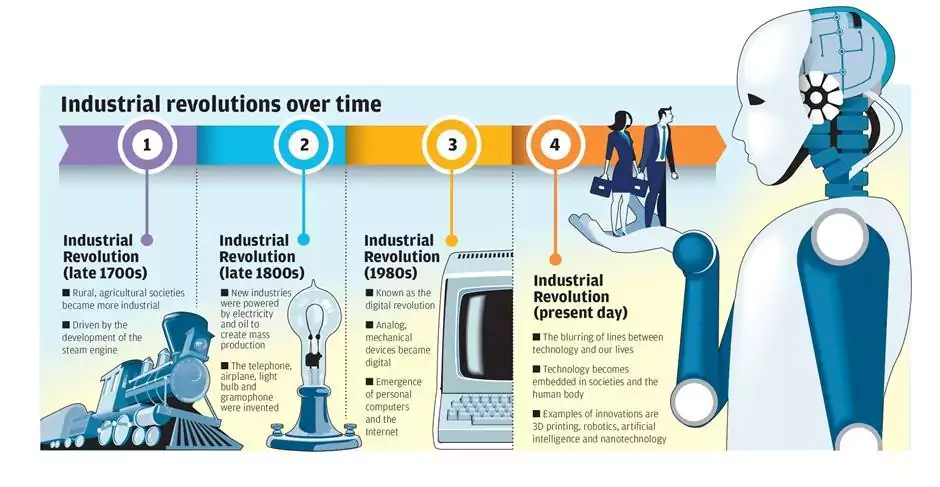
2.What are the processes of manufacturing?

The manufacturing process usually consists of the following major segments:
* Design: Formation and refinement of the product concept.
* Raw Material Procurement: Selection of suitable materials to meet design requirements.
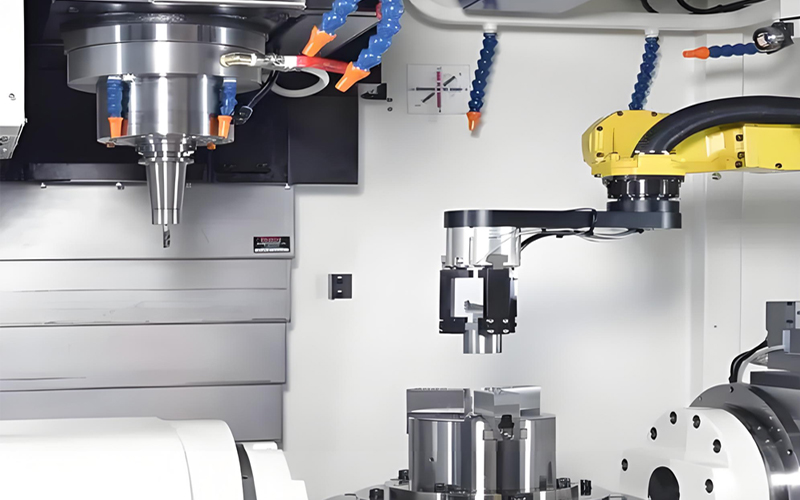
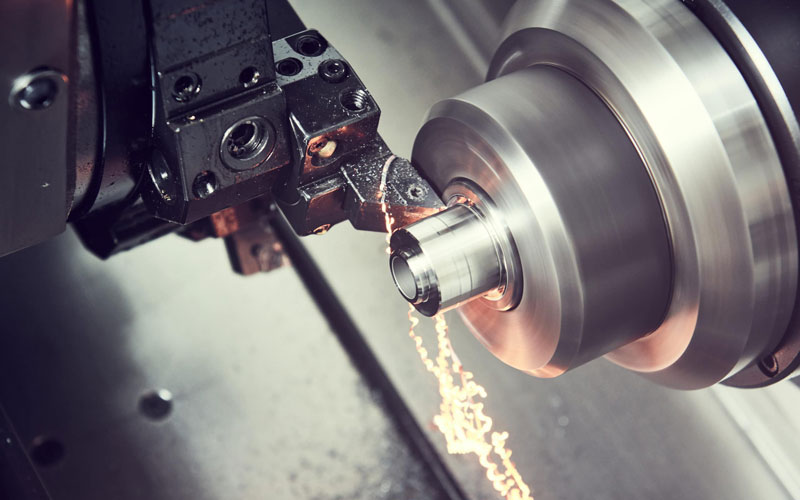
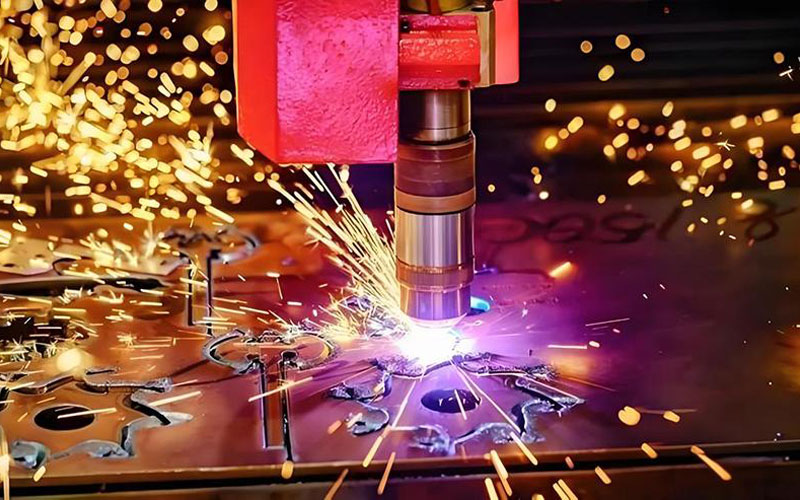
* Processing: Utilizing mechanical equipment to transform raw materials into semi-finished or finished products.
* Assembly: assembling multiple components into a final product.
* Quality control: ensuring that the product meets standards and specifications.