The Ultimate Guide to CNC Machining
Everything you need to know about CNC machining, from the basics to advanced design tips. Find all answers for your custom manufacturing needs.
Are you struggling to get those perfect custom parts? Do you wonder how complex designs come to life with incredible precision? CNC machining is your answer.This guide will walk you through everything, from the basics to advanced options.
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining stands for Computer Numerical Control machining. It uses programmed computer software to control the movement of factory tools and machinery. This allows for automated, highly precise manufacturing of parts, making it essential for producing complex geometries and achieving tight tolerances across various industries.
Types of CNC Machines
Are you wondering about the different types of CNC machines? Do you want to know what each one does best?
There are several types of CNC machines, each designed for specific tasks. Common types include CNC mills, which use rotating cutting tools to remove material; CNC lathes (turning machines), which rotate the workpiece against a cutting tool; and CNC routers, often used for larger, softer materials. Each machine type offers unique capabilities for shaping various parts.
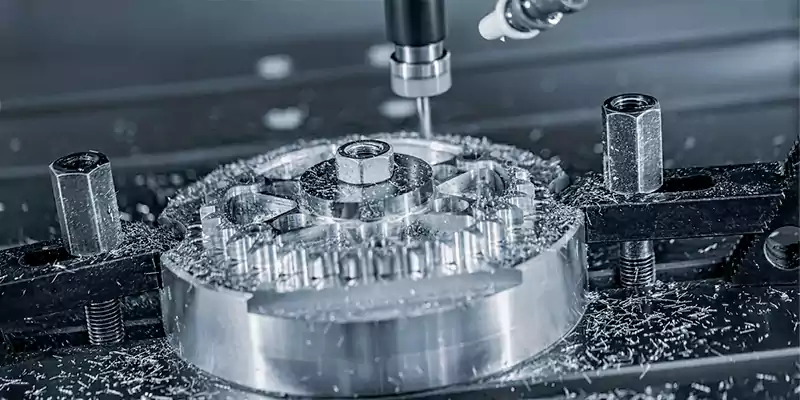

CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines use rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece. They can produce a wide range of shapes with high precision.
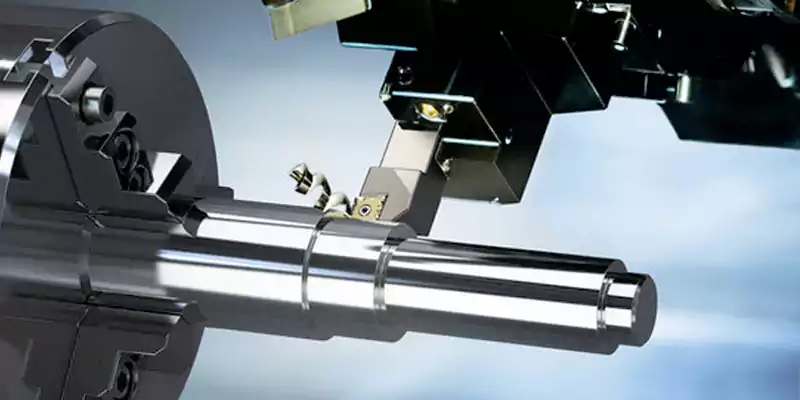
CNC Lathes (Turning Machines)
CNC lathes rotate the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool removes material. Ideal for producing cylindrical parts with rotational symmetry.
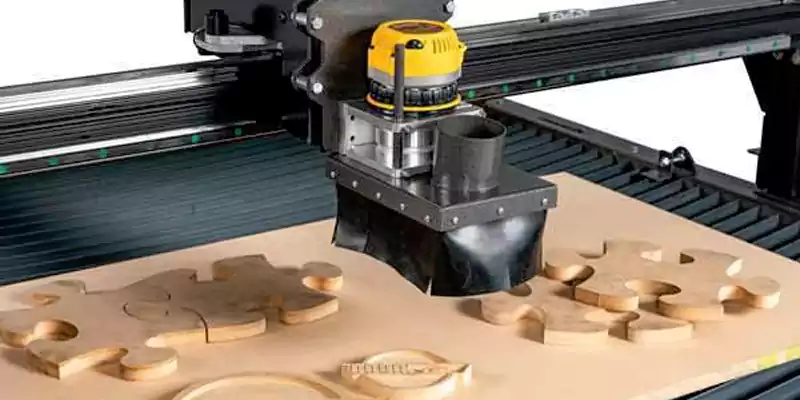

CNC Routers
CNC routers use high-speed cutters to process wood, plastics, and soft metals. They are ideal for making complex shapes and large parts with precision.
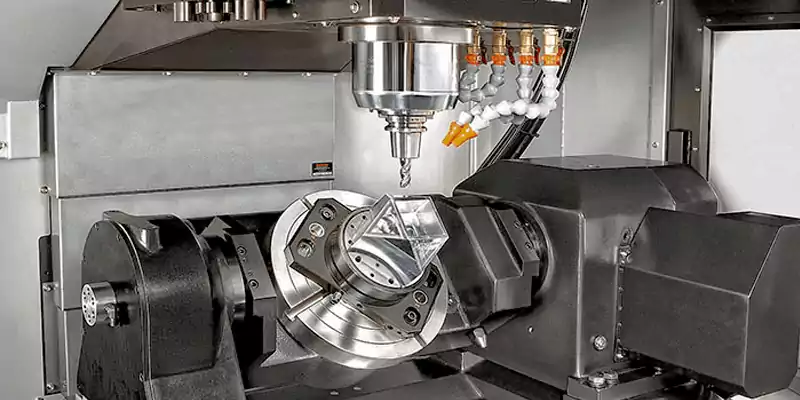

5-axis CNC Machine
5-axis machines can move tools in five different directions simultaneously, allowing for the production of highly complex parts in a single setup.
CNC Machining Processes
CNC machining involves several processes, each suited for different outcomes. Key processes include CNC milling, where material is removed by rotating cutters; CNC turning, which shapes cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece; and CNC drilling, for creating holes. Other methods like grinding, boring, and tapping further refine parts or add specific features, ensuring a comprehensive approach to part creation.
CNC Milling
This process removes material using rotating multi-point cutting tools.
- Face Milling: Creates flat surfaces.
- Peripheral Milling: Shapes the sides of a workpiece.
- Slotting: Cuts narrow channels.
CNC Turning
Turning involves rotating the workpiece against a single-point cutting tool.
- Facing: Smooths the end of a cylindrical part.
- Taper Turning: Creates conical shapes.
- Threading: Cuts internal or external screw threads.
CNC Drilling
Drilling creates round holes in the workpiece.
- Spot Drilling: Creates a shallow hole to guide a larger drill.
- Counterboring: Creates a flat-bottomed hole for a bolt head.
- Countersinking: Creates a conical hole for a flat-head screw.
Other Processes
- Grinding: Uses abrasive wheels for very fine surface finishes or tight tolerances.
- Boring: Enlarges existing holes to a precise diameter.
- Tapping: Creates internal threads in a hole.
Choosing the wrong process can be a costly mistake. Let’s take a closer look at the different CNC machining processes to see which one is the perfect fit for your needs.
Materials for CNC Machining
CNC machining can process a wide array of materials, from various metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium to different plastics such as ABS, Nylon, and Delrin, and even some specialized composites. The choice of material depends on the part’s required strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and specific application, allowing for highly customized solutions across industries.
Metals
Metals are very common in CNC machining due to their strength and durability.
- Aluminum (6061, 7075): Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance.
- Stainless Steel (303, 304, 316): High strength, corrosion resistance, good for medical and food industries.
- Steel (1018, A36): General purpose, strong, cost-effective.
- Titanium (Grade 2, Grade 5): Very high strength, lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatible.
Plastics
Plastics offer different properties like flexibility, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance.
- ABS: Good impact resistance, easily machined.
- Nylon: High strength, wear resistance, good for bearings and gears.
- Delrin (Acetal): Excellent stiffness, low friction, dimensionally stable.
- Polycarbonate: High impact strength, clear.
Specialized Materials
Sometimes, unique applications need special materials.
- Composites: Like carbon fiber, used for high strength and low weight.
- Exotic Alloys: Such as Inconel, for high-temperature and corrosive environments.
The performance of your final part truly depends on the material you start with. If you’re weighing the benefits of different metals or plastics for your specific application, you can explore our full range of machining materials.
CNC Machining Tools
Common CNC Machining Tool Types
While there are thousands of specialized tools, the vast majority of all CNC work is done with a few essential types. Each tool is designed for a specific operation, and using the right one for the job is a fundamental skill for any machinist. Understanding this helps bridge the gap between a digital design and a perfectly finished physical part.
Tool Type | Primary Use | Common Operations |
End Mill | The most versatile milling tool. | Creating pockets, slots, profiles, and complex 3D contours. |
Face Mill | Creating large, flat surfaces. | Facing the top of a workpiece to create a perfectly flat starting point. |
Drill Bit | Creating round holes. | Pre-drilling holes for tapping or creating clearance holes for bolts. |
Turning Insert | Shaping parts on a lathe. | Turning outer diameters, facing, grooving, and boring on cylindrical parts. |
For more information on CNC cutting tools, please visit the CNC Tools page directly.
Tool Materials and Coatings
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): This is a tough and affordable tool material, but it cannot handle the high speeds and temperatures of modern CNC machining. We typically use it for drilling or tapping operations.
- Solid Carbide: This is the standard for performance machining. Carbide is much harder and more wear-resistant than HSS, allowing it to cut at much higher speeds. This results in shorter cycle times and a better surface finish.
- Coated Carbide: Most of the high-performance tools we use today are solid carbide tools with an advanced coating (like Titanium Nitride – TiN, or Aluminum Titanium Nitride – AlTiN). These microscopic coatings are even harder than the carbide itself. They reduce friction, improve chip evacuation, and dramatically increase the tool’s lifespan, which is critical for maintaining consistency on production runs.
Surface Finishing Options
Surface finishing options for CNC machined parts are diverse, ranging from practical treatments like anodizing for corrosion resistance and powder coating for durability to aesthetic finishes like polishing for a smooth, reflective look. Other options include bead blasting for a matte texture, electroplating for enhanced properties, and specialized coatings, each offering unique benefits for protection, appearance, or functionality.

Anodizing
Anodizing creates a protective oxide layer on aluminum parts, improving corrosion resistance and allowing for coloring options.

Powder Coating
Powder coating applies a durable, protective layer that is resistant to chipping, scratching, and other forms of wear.

Bead Blasting
Bead blasting creates a uniform matte or satin surface finish, removing all visible tool marks from machined parts.

Polishing
Polishing produces a smooth, reflective surface finish that enhances appearance and reduces roughness on machined parts.

Electroplating
Electroplating deposits a thin metallic layer onto parts, improving wear resistance, corrosion protection, and decorative appeal.

Deburring
Deburring removes sharp edges and small imperfections, ensuring safer handling and improving the overall part quality.
Beyond these common choices, there’s a wide range of treatments available to meet specific functional or cosmetic needs. You can see a full breakdown of our capabilities in our complete guide to surface finishing.
Design for CNC Machining
Designing for CNC machining involves considering several key factors to ensure manufacturability and cost-efficiency. This includes adhering to proper tolerances for precision, selecting appropriate materials, optimizing part geometry to minimize machining time and complexity, and simplifying features. Effective design practices help avoid common machining challenges and ensure the final part meets functional and aesthetic requirements without unnecessary expense or delays.
Tolerances and Precision
Setting the right tolerances is crucial.
- Loose Tolerances: Cost-effective, suitable when high precision is not critical.
- Tight Tolerances: More expensive, required for critical fitments or high-performance parts.
Material Selection
The chosen material impacts design.
- Consider material strength, machinability, and cost.
- Design features to suit the material’s properties (e.g., wall thickness).
Part Geometry
Simpler geometries are easier and cheaper to machine.
- Avoid deep, narrow pockets or sharp internal corners.
- Use standard radii for internal corners where possible.
Minimizing Setups
Each time a part is repositioned, it adds cost and potential for error.
- Design parts that can be machined in one or two setups if possible.
- Use features that allow for easy clamping.
Our Capabilities
Allied Metal specializes in comprehensive CNC machining services, including advanced CNC milling and turning for complex geometries and tight tolerances. We also offer 3D printing for rapid prototyping and various rapid prototyping solutions.

CNC Machining Services
Precision three-axis to five-axis milling, suitable for various materials and complex parts.

3D Printing Services
Additive manufacturing for prototypes and complex geometries

Rapid Prototyping Services
Beyond 3D printing, we also offer other rapid prototyping methods to facilitate quick iterations.

Surface Finishing Services
We provide post-processing, plating, anodizing, powder coating, shot blasting, and other services.
Why Choose Allied Metal?
- Precision and Quality: We ensure every part meets stringent specifications.
- Efficiency and Speed: We optimize our processes to deliver quickly.
- Cost Effectiveness: We aim to provide value without compromising quality.
- Customer Focus: Our clients are at the heart of what we do.
FAQ
Standard lead times are 5-10 days for most projects, but we offer expedited services for urgent projects with lead times as short as 2-3 days.
We accept STEP, IGES, SLDPRT, and X_T file formats for CNC machining. For the best results, please provide 3D CAD files along with 2D drawings for critical dimensions.
We work with a wide range of metals including aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass, and titanium, as well as engineering plastics like ABS, Nylon, POM, Polycarbonate, and PEEK.
Yes, we offer a variety of surface finishing options including anodizing, powder coating, bead blasting, polishing, and silk screening to meet your specific requirements.
Didn’t find the solution you were looking for? No worries—continue reading our comprehensive CNC machining FAQ or contact us directly for machining details or a quote.
Ready to Start Your CNC Machining Project?
Get an instant quote and start manufacturing with Allied Metal’s advanced capabilities and expertise.
