Understanding 5-Axis CNC Machining: Definitions, Principles, Benefits and Applications
- March 1, 2025
- Tony
- Last updated on October 22, 2025 by Lucy

1. Overview
What is 5-Axis CNC Machining?
5-axis CNC machining is a high-precision manufacturing technology that realizes simultaneous operation in five directions by a CNC machine tool, and is suitable for machining parts with complex shapes and extremely high precision requirements.
Unlike traditional 3-axis machining, 5-axis machining is able to complete multi-angle cutting on a single fixture, which greatly enhances the flexibility and efficiency of machining.

Basic Principles
The basic principle of 5-axis CNC machining is to carry out all-round tool operation through the five axes of motion of the CNC machine tool – three linear axes (X, Y, Z axis) and two rotary axes (A axis, B axis).
Through this multi-dimensional cutting, 5-axis CNC machines are able to efficiently machine complex parts, especially those shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional machining methods, on the basis of a fixed workpiece.
2. How 5-Axis CNC Machining Works?
The workings of a 5-axis CNC machine involve several key aspects:
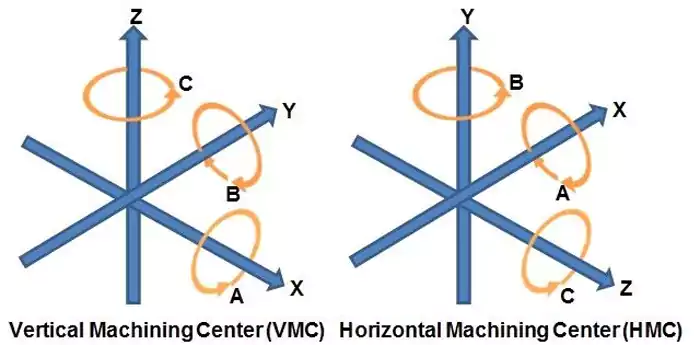
Multi-axis Motion Control
A 5-axis CNC machine uses three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotary axes (A, B), enabling tools and workpieces to move in multiple directions at once. This capability allows for the machining of complex shapes, like beveled and curved surfaces.
Coordinate System Adjustment
The machine operates with a precise coordinate system to control the movement of each axis. This flexibility lets the machine adjust the workpiece’s machining direction in space, ensuring high precision when positioning tools at various angles.
Tool Path Planning
Through the CNC program (G-code ), the machine calculates accurate tool paths based on the workpiece shape and task requirements. These paths allow for simultaneous movement along multiple axes, minimizing manual adjustments and reducing machining errors.
Synchronized Control
Real-time monitoring of all five axes ensures synchronized movement throughout the machining process. This control allows for precise adjustments, particularly when working with complex parts, ensuring the tool angle is correctly set while the workpiece remains fixed.
Precision Positioning and Feedback
Equipped with encoders and sensors , the 5-axis machine provides continuous feedback on each axis’s position. This system enables dynamic adjustments, ensuring machining accuracy and optimal surface quality throughout the process.
3. Core advantages of 5-axis CNC machining
Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency

5-axis CNC machines reduce errors and improve stability by machining in multiple directions with a single clamping. This also cuts down tool change and positioning times, boosting productivity.
Machining Complex Shapes

Ideal for complex parts like those in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries, 5-axis machining handles curved and beveled surfaces that traditional machines can’t manage, offering precise results.
Reduced machining times and processes
By operating in multiple directions at once, 5-axis machining cuts down on tool changes and adjustments, saving time and costs. Many CNC manufacturers further optimize their processes to enhance efficiency.
4. 5-Axis CNC Machining Applications
The precision and efficiency of the 5-axis machine tool manufacturing process has led to a wide range of applications in several industries:
Aerospace
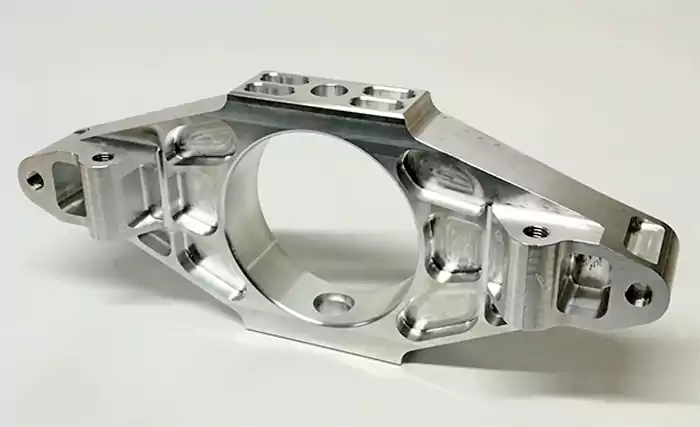

Due to the complex structure of aerospace parts and the extremely high requirements for precision, high-precision 5-axis machining has become an important tool in the field of aerospace manufacturing.
Automotive
In the manufacture of automotive parts, 5-axis machines are able to accurately machine engine components, body parts and other complex shapes to enhance production flexibility.
Medical equipment

The medical industry has very strict requirements for precision, and 5-axis CNC machining technology can meet the demand for high-precision machining of medical equipment components.
Mechanical equipment

5-axis CNC machining technology provides a stable and efficient CNC machining solution for high-strength, complex-shaped mechanical equipment components.
5. Case Study: Complex Impeller Manufacturing for Aerospace Applications
Below is a case study of a 5-axis machining project for a custom impeller produced in our workshop. This titanium alloy aircraft engine impeller would have been nearly impossible to manufacture using traditional 3-axis equipment.
The Challenge: Our client needed a high-performance impeller with complex blade geometries that demanded extreme precision. The blades featured compound curves and needed to maintain consistent wall thicknesses while handling intense rotational forces.
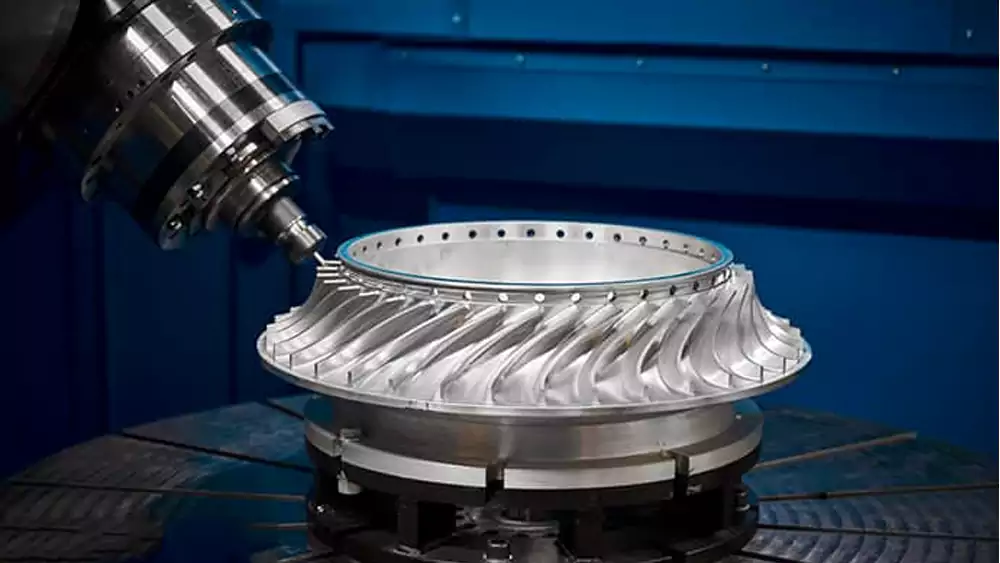

Our 5-Axis Solution: We tackled this project using our Hermle C 42 U 5-axis machining center.
Here are the key parameters that made this job successful:
- Material: Aerospace-grade Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy
- Overall Dimensions: 280mm diameter × 150mm height
- Blade Count: 18 primary blades with 18 splitter blades
- Tightest Tolerance: ±0.015mm on blade profile dimensions
- Surface Finish : Ra 0.4μm on aerodynamic surfaces
- Thinnest Section: 0.8mm blade edges
- Machining Time: 14.5 hours complete (compared to estimated 28+ hours with 3-axis)
- Tooling: Used 12 different cutting tools with maximum 8mm diameter for fine details
- Setup Advantage: Single setup eliminated cumulative errors from multiple repositioning
The Result: The part came off the machine with perfect blade geometry and required only minimal hand polishing. The single setup approach eliminated the stacking errors we would have faced with multiple repositioning. Most importantly, the client’s testing showed a 3% efficiency improvement over their previous supplier’s parts due to better surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
This is exactly the kind of work where 5-axis machining pays for itself – complex geometries, tight tolerances, and difficult materials all handled in one efficient operation.
6. Operating Tips and Cautions
1. Pre-machining Preparation and Setup
Before starting, proper preparation is key:
- Determine the Part Details: Identify the material, size, and machining requirements.
- Choose Tools and Settings: Select the right tools and machining parameters based on the part details.
- Clear Communication: When working with CNC machining service providers , provide clear design drawings and specifications to ensure an accurate machining plan.
2. Workpiece Fixation and Tool Selection
Stability and the right tools are crucial for success:
- Fix the Workpiece: Ensure the workpiece is securely held in place to prevent any movement during machining.
- Select Fixtures: Use the appropriate fixtures and clamping methods for stability and accuracy.
- Choose Tools Wisely: Pick tools that match the material, shape, and complexity of the part for the best results.
3. Monitoring and Adjustment During Machining
Continuous monitoring ensures quality:
- Watch the Process: Keep an eye on tool wear and machining accuracy throughout the process.
- Make Adjustments: CNC machining service providers often offer real-time monitoring to adjust the process and maintain optimal results.
7. FAQ about 5-axis machining
Tool wear
Tools are prone to wear due to high loads, affecting accuracy and surface quality. Regular monitoring and timely tool replacement can resolve this issue.
Workpiece Deformation
Workpieces may deform from cutting forces or poor clamping. Secure clamping and proper cutting parameters help minimize deformation.
Machining accuracy deviation
Accuracy deviations can occur due to machine errors or incorrect parameters. Regular calibration and process monitoring can improve accuracy.
Tool Collisions
Tool collisions are common in complex machining. Proper tool path planning, compensation techniques, and simulation checks can prevent collisions.
Program Errors and Programming Problems
Programming errors can lead to machining issues. Reviewing the program, running simulations, and multiple checks can prevent problems.
Thermal deformation
High-speed cutting generates heat that can cause thermal deformation. Using efficient coolant and adjusting cutting speeds can reduce this issue.
Insufficient machine stability
Lack of machine stability or poor maintenance can cause vibrations and affect quality. Regular machine inspections and maintenance prevent this problem.
8.Future development trend
Advancements in technology will drive the growth of 5-axis CNC machining, with intelligent automation playing a key role. In the future, CNC service providers will use smart machines that can automatically monitor and adjust accuracy and process parameters, enhancing both precision and efficiency.
As automation rises, 5-axis machining will become more efficient, reducing the need for manual intervention. This evolution will make 5-axis CNC machining an increasingly precise, efficient, and cost-effective solution for various industries.

